Neuroinflammatory Gene Expression Pattern Is Similar between Allergic Rhinitis and Atopic Dermatitis but Distinct from Atopic Asthma
- PMID: 32596360
- PMCID: PMC7305544
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7196981
Neuroinflammatory Gene Expression Pattern Is Similar between Allergic Rhinitis and Atopic Dermatitis but Distinct from Atopic Asthma
Abstract
Methods: In the study, we included 86 children diagnosed with atopic asthma (n = 25), allergic rhinitis (n = 20), and atopic dermatitis (n = 20) and healthy control subjects (n = 21) of Caucasian origin from the Polish population. The blood leukocyte expression of 31 genes involved in neuroinflammatory response (neurotrophins, their receptors, neuropeptides, and histamine signaling pathway) was analysed using TaqMan low-density arrays. The relative expression of selected proteins from plasma was done using TaqMan Protein Assays. Statistical analysis was done using Statistica.
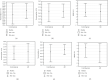
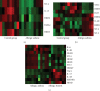
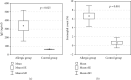
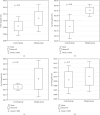
Results: Blood expression of 31 genes related to neuroimmune interactions showed significant increase in both allergic diseases, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis, in comparison to the control group. We found 12 genes significantly increased in allergic rhinitis and 9 genes in which the expression was elevated in atopic dermatitis. Moreover, 9 genes with changed expression in atopic dermatitis overlapped with those in allergic rhinitis. Atopic asthma showed 5 genes with altered expression. The peripheral expression of neuroinflammatory genes in the human study was verified in target tissues (nasal epithelium and skin) in a rat model of allergic inflammation.
Conclusions: A common pattern of neuroinflammatory gene expression between allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis may reflect similar changes in sensory nerve function during chronic allergic inflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Paulina Sobkowiak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neurotrophins: Neuroimmune Interactions in Human Atopic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6105. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076105. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALLERGIC DISEASES AND ASTHMA IN ADOLESCENTS.Georgian Med News. 2015 Jun;(243):58-62. Georgian Med News. 2015. PMID: 26087732
-
Familial aggregation of atopic dermatitis and co-aggregation of allergic diseases in affected families in Taiwan.J Dermatol Sci. 2020 Oct;100(1):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.07.007. Epub 2020 Aug 10. J Dermatol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32873424
-
Association of Circadian Clock Gene Expression with Pediatric/Adolescent Asthma and Its Comorbidities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 19;24(8):7477. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087477. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108640 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of New IL-1 Family Members (IL-36 and IL-38) in Atopic Dermatitis, Allergic Asthma, and Allergic Rhinitis.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020 Jun 12;20(8):40. doi: 10.1007/s11882-020-00937-1. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020. PMID: 32533268 Review.
Cited by
-
[Neuroimmunomodulation in allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Sep;35(9):859-864. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.09.021. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34628846 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Network pharmacology integrated with molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations to explore the mechanism of Shaoyao Gancao Tang in the treatment of asthma and irritable bowel syndrome.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 13;103(50):e40929. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040929. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39686413 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Study of Yupingfeng Powder in the Treatment of Allergic Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 9;2022:1323744. doi: 10.1155/2022/1323744. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35855823 Free PMC article.
-
The Singapore/Malaysia Cross-Sectional Genetics Epidemiology Study: An Updated and Detailed Analysis of Acne Vulgaris Severity, Scarring, and Phenotypes and Their Associated Risk Factors among Young Chinese Adults.Dermatology. 2025 Jun 17:1-15. doi: 10.1159/000547009. Online ahead of print. Dermatology. 2025. PMID: 40527305 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor causes epinephrine release dysfunction by regulating phenotype alterations and the function of adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in mice with allergic rhinitis.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Feb;27(2):39. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.12926. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36601769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raap U., Deneka N., Bruder M., Kapp A., Wedi B. Differential up-regulation of neurotrophin receptors and functional activity of neurotrophins on peripheral blood eosinophils of patients with allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and nonatopic subjects. Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 2008;38(9):1493–1498. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03035.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

