Toll interacting protein protects bronchial epithelial cells from bleomycin-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 32596871
- PMCID: PMC8175118
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201902636RR
Toll interacting protein protects bronchial epithelial cells from bleomycin-induced apoptosis
Abstract
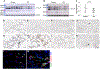
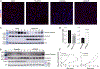
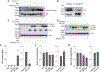
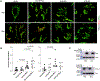
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is characterized by altered epithelial cell phenotypes, which are associated with myofibroblast accumulation in the lung. Atypical alveolar epithelial cells in IPF express molecular markers of airway epithelium. Polymorphisms within and around Toll interacting protein (TOLLIP) are associated with the susceptibility to IPF and mortality. However, the functional role of TOLLIP in IPF is unknown. Using lung tissues from IPF and control subjects, we showed that expression of TOLLIP gene in the lung parenchyma is globally lower in IPF compared to controls. Lung cells expressing significant levels of TOLLIP include macrophages, alveolar type II, and basal cells. TOLLIP protein expression is lower in the parenchyma of IPF lungs but is expressed in the atypical epithelial cells of the distal fibrotic regions. Using overexpression and silencing approaches, we demonstrate that TOLLIP protects cells from bleomycin-induced apoptosis using primary bronchial epithelial cells and BEAS-2B cells. The protective effects are mediated by reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and upregulating autophagy. Therefore, global downregulation of the TOLLIP gene in IPF lungs may predispose injured lung epithelial cells to apoptosis and to the development of IPF.
Keywords: TOLLIP; apoptosis; autophagy; basal cells; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung epithelial cells.
© 2020 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures


References
-
- King TE Jr., Schwarz MI, Brown K, Tooze JA, Colby TV, Waldron JA Jr., Flint A, Thurlbeck W, and Cherniack RM (2001) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: relationship between histopathologic features and mortality. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 164, 1025–1032 - PubMed
-
- Selman M, and Pardo A (2003) The epithelial/fibroblastic pathway in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology 29, S93–97 - PubMed
-
- Selman M, and Pardo A (2006) Role of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: from innocent targets to serial killers. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 3, 364–372 - PubMed
-
- Prasse A, Binder H, Schupp JC, Kayser G, Bargagli E, Jaeger B, Hess M, Rittinghausen S, Vuga L, Lynn H, Violette S, Jung B, Quast K, Vanaudenaerde B, Xu Y, Hohlfeld JM, Krug N, Herazo-Maya JD, Rottoli P, Wuyts WA, and Kaminski N (2019) BAL Cell Gene Expression Is Indicative of Outcome and Airway Basal Cell Involvement in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 199, 622–630 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

