Efficient Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of N-Glycans with a β1,4-Galactosylated Bisecting GlcNAc Motif
- PMID: 32597008
- PMCID: PMC7723014
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202000268
Efficient Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of N-Glycans with a β1,4-Galactosylated Bisecting GlcNAc Motif
Abstract
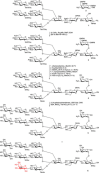
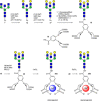
In human serum immunoglobulin G (IgG), a rare modification of biantennary complex N-glycans lead to a β1,4-galactosylated bisecting GlcNAc branch. We found that the bisecting GlcNAc on a biantennary core-fucosylated N-glycan was enzymatically galactosylated under stringent reaction conditions. Further optimizations led to an efficient enzymatic approach to this particular modification for biantennary substrates. Notably, tri- and tetra-antennary complex N-glycans were not converted by bovine galactosyltransferase. An N-glycan with a galactosylated bisecting GlcNAc was linked to a lanthanide binding tag. The pseudo-contact shifts (PCS) obtained from the corresponding Dy-complex were used to calculate the conformational preferences of the rare N-glycan. Besides two extended conformations only a single folded conformation was found.
Keywords: N-glycans; glycobiology; glycosylation; immunoglobulin; paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- None
-
- Shinkawa T., Nakamura K., Yamane N., Shoji-Hosaka E., Kanda Y., Sakurada M., Uchida K., Anazawa H., Satoh M., Yamasaki M., Hanai N., Shitara K., J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3466–3473; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

