Interpretation challenges of novel dual-class missense and splice-impacting variant in POLR3A-related late-onset hereditary spastic ataxia
- PMID: 32597037
- PMCID: PMC7507001
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1341
Interpretation challenges of novel dual-class missense and splice-impacting variant in POLR3A-related late-onset hereditary spastic ataxia
Abstract
Background: RNA polymerase III (Pol III)-related disorders are autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorders caused by variants in POLR3A or POLR3B. Recently, a novel phenotype of adult-onset spastic ataxia was identified in individuals with the c.1909+22G>A POLR3A variant in compound heterozygosity.
Methods: Whole-exome sequencing was performed in the proband and parents. Variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. RNA sequencing was performed to evaluate splicing implications.
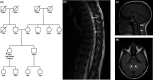
Results: A 42-year-old female was evaluated for unexplained neurological findings with a slow progressive decline in gait and walking speed since adolescence. WES revealed a novel missense variant (c.3593A>C, p.Lys1198Arg) in exon 27 of POLR3A in compound heterozygosity with the c.1909+22G>A variant. Summary of previously reported clinical features from individuals with pathogenic biallelic alterations in POLR3A and adult-onset phenotype is consistent with our findings. RNA analysis revealed c.3593A>G drives the production of four RNA transcript products each with different functional impacts.
Conclusion: The novel dual-class c.3593A>C variant in POLR3A causes an amino acid substitution and complex disruption of splicing. Our report supports the need to investigate variants near splice junctions for proper interpretation. Current interpretation guidelines need to address best practices for inclusion of predicted or measured transcriptional disruption pending functional activity or reliable transcript abundance estimates.
Keywords: bioinformatics; missense; splicing; variant interpretation.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Abou Tayoun, A. N. , Pesaran, T. , DiStefano, M. T. , Oza, A. , Rehm, H. L. , Biesecker, L. G. … ClinGen Sequence Variant Interpretation Working, G. (2018). Recommendations for interpreting the loss of function PVS1 ACMG/AMP variant criterion. Human Mutation, 39(11), 1517–1524. 10.1002/humu.23626 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azmanov, D. N. , Siira, S. J. , Chamova, T. , Kaprelyan, A. , Guergueltcheva, V. , Shearwood, A. J. , … Filipovska, A. (2016). Transcriptome‐wide effects of a POLR3A gene mutation in patients with an unusual phenotype of striatal involvement. Human Molecular Genetics, 25(19). 10.1093/hmg/ddw263 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernard, G. , Chouery, E. , Putorti, M. L. , Tétreault, M. , Takanohashi, A. , Carosso, G. , … Brais, B. (2011). Mutations of POLR3A encoding a catalytic subunit of RNA polymerase Pol III cause a recessive hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. American Journal of Human Genetics, 89(3), 415–423. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.07.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choquet, K. , Forget, D. , Meloche, E. , Dicaire, M. J. , Bernard, G. , Vanderver, A. , … Kleinman, C. L. (2019). Leukodystrophy‐associated POLR3A mutations down‐regulate the RNA polymerase III transcript and important regulatory RNA BC200. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294(18). 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006271 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

