Alzheimer's Disease: The Link Between Amyloid-β and Neurovascular Dysfunction
- PMID: 32597813
- PMCID: PMC7483596
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-200473
Alzheimer's Disease: The Link Between Amyloid-β and Neurovascular Dysfunction
Abstract
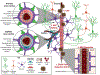
While prevailing evidence supports that the amyloid cascade hypothesis is a key component of Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology, many recent studies indicate that the vascular system is also a major contributor to disease progression. Vascular dysfunction and reduced cerebral blood flow (CBF) occur prior to the accumulation and aggregation of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau tangles. Although research has predominantly focused on the cellular processes involved with Aβ-mediated neurodegeneration, effects of Aβ on CBF and neurovascular coupling are becoming more evident. This review will describe AD vascular disturbances as they relate to Aβ, including chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, hypertension, altered neurovascular coupling, and deterioration of the blood-brain barrier. In addition, we will describe recent findings about the relationship between these vascular defects and Aβ accumulation with emphasis on in vivo studies utilizing rodent AD models.
Keywords: Amyloid-β peptide; amyloid cascade hypothesis; blood-brain barrier; cerebral amyloid angiopathy; chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; functional hyperemia; in vivo mouse model; in vivo rat model; neurovascular coupling; vascular hypothesis.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association (2019) 2019 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 15, 321–387.
-
- Swerdlow RH (2007) Is aging part of Alzheimer’s disease, or is Alzheimer’s disease part of aging? Neurobiol Aging 28, 1465–1480. - PubMed
-
- Katzman R (1976) Editorial: The prevalence and malignancy of Alzheimer disease. A major killer. Arch Neurol 33, 217–218. - PubMed
-
- Iwatsubo T, Odaka A, Suzuki N, Mizusawa H, Nukina N, Ihara Y (1994) Visualization of A beta 42(43) and A beta 40 in senile plaques with end-specific A beta monoclonals: Evidence that an initially deposited species is A beta 42(43). Neuron 13, 45–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

