Asymmetric dimerization of adenosine deaminase acting on RNA facilitates substrate recognition
- PMID: 32597966
- PMCID: PMC7641318
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa532
Asymmetric dimerization of adenosine deaminase acting on RNA facilitates substrate recognition
Abstract
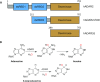
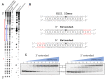
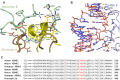
Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) are enzymes that convert adenosine to inosine in duplex RNA, a modification that exhibits a multitude of effects on RNA structure and function. Recent studies have identified ADAR1 as a potential cancer therapeutic target. ADARs are also important in the development of directed RNA editing therapeutics. A comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanism of the ADAR reaction will advance efforts to develop ADAR inhibitors and new tools for directed RNA editing. Here we report the X-ray crystal structure of a fragment of human ADAR2 comprising its deaminase domain and double stranded RNA binding domain 2 (dsRBD2) bound to an RNA duplex as an asymmetric homodimer. We identified a highly conserved ADAR dimerization interface and validated the importance of these sequence elements on dimer formation via gel mobility shift assays and size exclusion chromatography. We also show that mutation in the dimerization interface inhibits editing in an RNA substrate-dependent manner for both ADAR1 and ADAR2.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Grosjean H., Grosjean H.. 2005; Springer.
-
- Rueter S.M., Dawson T.R., Emeson R.B.. Regulation of alternative splicing by RNA editing. Nature. 1999; 399:75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

