The epitranscriptome landscape of small noncoding RNAs in stem cells
- PMID: 32598085
- PMCID: PMC7586957
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.3233
The epitranscriptome landscape of small noncoding RNAs in stem cells
Abstract
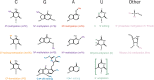
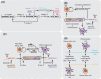
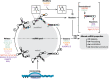
Stem cells (SCs) are unique cells that have an inherent ability to self-renew or differentiate. Both fate decisions are strongly regulated at the molecular level via intricate signaling pathways. The regulation of signaling networks promoting self-renewal or differentiation was thought to be largely governed by the action of transcription factors. However, small noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as vault RNAs, and their post-transcriptional modifications (the epitranscriptome) have emerged as additional regulatory layers with essential roles in SC fate decisions. RNA post-transcriptional modifications often modulate RNA stability, splicing, processing, recognition, and translation. Furthermore, modifications on small ncRNAs allow for dual regulation of RNA activity, at both the level of biogenesis and RNA-mediated actions. RNA post-transcriptional modifications act through structural alterations and specialized RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) called writers, readers, and erasers. It is through SC-context RBPs that the epitranscriptome coordinates specific functional roles. Small ncRNA post-transcriptional modifications are today exploited by different mechanisms to facilitate SC translational studies. One mechanism readily being studied is identifying how SC-specific RBPs of small ncRNAs regulate fate decisions. Another common practice of using the epitranscriptome for regenerative applications is using naturally occurring post-transcriptional modifications on synthetic RNA to generate induced pluripotent SCs. Here, we review exciting insights into how small ncRNA post-transcriptional modifications control SC fate decisions in development and disease. We hope, by illustrating how essential the epitranscriptome and their associated proteome are in SCs, they would be considered as novel tools to propagate SCs for regenerative medicine.
Keywords: adult stem cells; cancer stem cells; epigenetics; epitranscriptome; microRNAs; noncoding RNAs.
©2020 The Authors. Stem Cells published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. on behalf of AlphaMed Press 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zhu Y, Uezono N, Yasui T, Nakashima K. Neural stem cell therapy aiming at better functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Dev Dyn. 2018;247(1):75‐84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

