Learning opportunities from COVID-19 and future effects on health care system
- PMID: 32599533
- PMCID: PMC7305503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.036
Learning opportunities from COVID-19 and future effects on health care system
Abstract
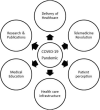
Background and aims: COVID-19 has had a crippling effect on the health care systems around the world with cancellation of elective medical services and disruption of daily life. We would like to highlight the learning opportunities offered by the current pandemic and their implication for a better future health care system.
Methods: We have undertaken a comprehensive review of the current literature to analyse the consequences of COVID-19 on health care system. Using suitable keywords like 'COVID-19', 'telemedicine', 'health care' and 'remote consultations' on the search engines of PubMed, SCOPUS, Google Scholar and Research Gate in the first week of May we gathered information on various aspects of effect of COVID-19.
Results: There has been a shared drive worldwide to devise strategies to protect people against viral transmission with reinforcement of hand hygiene and infection control principles but also to provide continuity of health care. Virtual and remote technologies have been increasingly used in health care management.
Conclusion: COVID-19 has offered unique learning opportunities for the health care sector. Rationalizing and optimizing available resources with resilience shown on the coronavirus frontline during the crisis are some of most important lessons learnt during the crisis. Importance of personal hygiene and re-enforcement of infection control measures have been acknowledged. Telemedicine revolution will be a vital factor in delivering health care in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Health care systems; Pandemics; Telemedicine.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation Dashboard Coronavirus 2020. https://experience.arcgis.com/experience/685d0ace521648f8a5beeeee1b9125cd accessed 17 May 2020.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/index.html
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-f...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical