Biofilm formation on three different endotracheal tubes: a prospective clinical trial
- PMID: 32600373
- PMCID: PMC7322705
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-03092-1
Biofilm formation on three different endotracheal tubes: a prospective clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Biofilm formation on endotracheal tubes (ETTs) is an early and frequent event in mechanically ventilated patients. The biofilm is believed to act as a reservoir for infecting microorganisms and thereby contribute to development and relapses of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). Once a biofilm has formed on an ETT surface, it is difficult to eradicate. This clinical study aimed to compare biofilm formation on three widely used ETTs with different surface properties and to explore factors potentially predictive of biofilm formation.
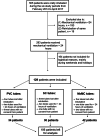
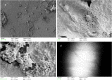
Methods: We compared the grade of biofilm formation on ETTs made of uncoated polyvinyl chloride (PVC), silicone-coated PVC, and PVC coated with noble metals after > 24 h of mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients. The comparison was based on scanning electron microscopy of ETT surfaces, biofilm grading, surveillance and biofilm cultures, and occurrence of VAP.
Results: High-grade (score ≥ 7) biofilm formation on the ETTs was associated with development of VAP (OR 4.17 [95% CI 1.14-15.3], p = 0.031). Compared to uncoated PVC ETTs, the silicone-coated and noble-metal-coated PVC ETTs were independently associated with reduced high-grade biofilm formation (OR 0.18 [95% CI 0.06-0.59], p = 0.005, and OR 0.34 [95% CI 0.13-0.93], p = 0.036, respectively). No significant difference was observed between silicon-coated ETTs and noble-metal-coated ETTs (OR 0.54 [95% CI 0.17-1.65], p = 0.278). In 60% of the oropharyngeal cultures and 58% of the endotracheal cultures collected at intubation, the same microorganism was found in the ETT biofilm at extubation. In patients who developed VAP, the causative microbe remained in the biofilm in 56% of cases, despite appropriate antibiotic therapy. High-grade biofilm formation on ETTs was not predicted by either colonization with common VAP pathogens in surveillance cultures or duration of invasive ventilation.
Conclusion: High-grade biofilm formation on ETTs was associated with development of VAP. Compared to the uncoated PVC ETTs, the silicone-coated and noble-metal-coated PVC ETTs were independently associated with reduced high-grade biofilm formation. Further research on methods to prevent, monitor, and manage biofilm occurrence is needed.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02284438 . Retrospectively registered on 21 October 2014.
Keywords: Alloys; Biofilm; Critical illness; Intratracheal; Intubation; Pneumonia; Polyvinyl chloride; Silicones; Ventilator-associated.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was performed as part of a national project entitled Innovation against Infection (in Swedish:
Figures
Comment in
-
Above and beyond: biofilm and the ongoing search for strategies to reduce ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).Crit Care. 2020 Aug 18;24(1):510. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03234-5. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32811553 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Melsen WG, Rovers MM, Koeman M, Bonten MJM. Estimating the attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia from randomized prevention studies. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:2736–2742. - PubMed
-
- Kollef MH, Hamilton CW, Ernst FR. Economic impact of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a large matched cohort. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012;33:250–256. - PubMed
-
- Muscedere JG, Day A, Heyland DK. Mortality, attributable mortality, and clinical events as end points for clinical trials of ventilator-associated pneumonia and hospital-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:120–125. - PubMed
-
- Melsen WG, Rovers MM, Groenwold RHH, Bergmans DCJJ, Camus C, Bauer TT, et al. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised prevention studies. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:665–671. - PubMed
-
- Morris AC, Hay AW, Swann DG, Everingham K, McCulloch C, McNulty J, et al. Reducing ventilator-associated pneumonia in intensive care: impact of implementing a care bundle. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:2218–2224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

