Tim-3 finds its place in the cancer immunotherapy landscape
- PMID: 32601081
- PMCID: PMC7326247
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000911
Tim-3 finds its place in the cancer immunotherapy landscape
Abstract
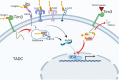
The blockade of immune checkpoint receptors has made great strides in the treatment of major cancers, including melanoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, renal, and lung cancer. However, the success rate of immune checkpoint blockade is still low and some cancers, such as microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer, remain refractory to these treatments. This has prompted investigation into additional checkpoint receptors. T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (Tim-3) is a checkpoint receptor expressed by a wide variety of immune cells as well as leukemic stem cells. Coblockade of Tim-3 and PD-1 can result in reduced tumor progression in preclinical models and can improve antitumor T-cell responses in cancer patients. In this review, we will discuss the basic biology of Tim-3, its role in the tumor microenvironment, and the emerging clinical trial data that point to its future application in the field of immune-oncology.
Keywords: clinical trials as topic; costimulatory and inhibitory T-cell receptors; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ACA is a member of the SAB for Tizona Therapeutics, Compass Therapeutics, and Zumutor Biologics, and Astellas Global Pharma Development, which have interests in cancer immunotherapy. ACA and CS-P are inventors on patents related to Tim-3. CS-P is an employee of Novartis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
