Effects of 2D-Shear Wave Elastography on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in the Brains of Neonatal Mice and Exploration of the Mechanism
- PMID: 32601265
- PMCID: PMC7346754
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.924832
Effects of 2D-Shear Wave Elastography on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in the Brains of Neonatal Mice and Exploration of the Mechanism
Abstract
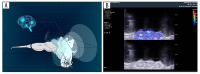
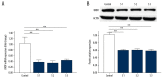
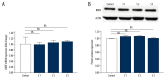
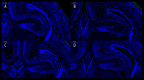
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to explore the effect and duration of 2-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) irradiation on the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the brains of neonatal mice and to preliminarily investigate whether its mechanism is neuronal apoptosis. MATERIAL AND METHODS Neonatal mice (within 48 hours of birth) were subjected to 2D-SWE irradiation of the brain for 10 minutes (group S1), 20 minutes (group S2), and 30 minutes (group S3). The mice were sacrificed immediately after irradiation or 24 hours after irradiation. Brains were collected for real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot experiments to determine the expression of BDNF in each group. TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) was performed to observe neuronal apoptosis in the brain. RESULTS The results of PCR and western blots from the brains of neonatal mice that were sacrificed immediately after irradiation show that S1, S2, and S3 were significantly different from those in the control group. The PCR and western blot results of brain tissues from neonatal mice sacrificed at 24 hours after irradiation showed that there was no significant difference between the S1, S2, S3, and control groups. The results of TUNEL experiments showed that there was no statistically significant difference in the number of apoptotic neurons between the S1, S2, S3, and control groups. CONCLUSIONS 2D-SWE irradiation of neonatal mice for more than 10 minutes downregulated the expression of BDNF. This effect disappeared within 24 hours after the irradiation, and the 2D-SWE scan seemed not to induce neuronal apoptosis.
Figures
References
-
- Su Y, Ma J, Du LF, et al. Evaluation of neonatal brain development using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) Neurophysiology. 2015;47(4):322–25. - PubMed
-
- Kim HG, Park MS, Lee JD, Park SY. Ultrasound elastography of the neonatal brain: preliminary study. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(7):1313–19. - PubMed
-
- Lalzad A, Wong F, Schneider M. Neonatal cranial ultrasound: Are current safety guidelines appropriate? Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017;43(3):553–60. - PubMed
-
- Unsworth T. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part H. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(7):i. - PubMed
-
- Li C, Zhang C, Li J, et al. An experimental study of the potential biological effects associated with 2-D shear wave elastography on the neonatal brain. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(7):1551–59. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

