WD repeat-containing protein 1 maintains β-Catenin activity to promote pancreatic cancer aggressiveness
- PMID: 32601462
- PMCID: PMC7492282
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-0929-0
WD repeat-containing protein 1 maintains β-Catenin activity to promote pancreatic cancer aggressiveness
Abstract
Background: The molecular signature underlying pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression may include key proteins affecting the malignant phenotypes. Here, we aimed to identify the proteins implicated in PDAC with different tumour-node-metastasis (TNM) stages.
Methods: Eight-plex isobaric tags coupled with two-dimensional liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry were used to analyse the proteome of PDAC tissues with different TNM stages. A loss-of-function study was performed to evaluate the oncogenic roles of WD repeat-containing protein 1 (WDR1) in PDAC. The molecular mechanism by which WDR1 promotes PDAC progression was studied by real-time qPCR, Western blotting, proximity ligation assay and co-immunoprecipitation.
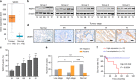
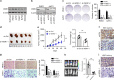
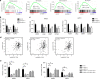
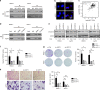
Results: A total of 5036 proteins were identified, and 4708 proteins were quantified with high confidence. Compared with normal pancreatic tissues, 37 proteins were changed significantly in PDAC tissues of different stages. Moreover, 64 proteins were upregulated or downregulated in a stepwise manner as the TNM stages of PDAC increased, and 10 proteins were related to tumorigenesis. The functionally uncharacterised protein, WDR1, was highly expressed in PDAC and predicted a poor prognosis. WDR1 knockdown suppressed PDAC tumour growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, WDR1 knockdown repressed the activity of the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway; ectopic expression of a stabilised form of β-Catenin restored the suppressive effects of WDR1 knockdown. Mechanistically, WDR1 interacted with USP7 to prevent ubiquitination-mediated degradation of β-Catenin.
Conclusion: Our study identifies several previous functional unknown proteins implicated in the progression of PDAC, and provides new insight into the oncogenic roles of WDR1 in PDAC development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 20;10:1304639. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1304639. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38174069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXO1-regulated lncRNA LINC01197 inhibits pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell proliferation by restraining Wnt/β-catenin signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 26;38(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1174-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31027497 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 promotes pancreatic cancer progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Sci Rep. 2019 May 17;9(1):7539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44048-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31101875 Free PMC article.
-
PRMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and predicts poor prognosis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Feb;43(1):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00435-1. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31520395
-
WNT Ligand Dependencies in Pancreatic Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 28;9:671022. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.671022. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33996827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TNK2-AS1 upregulated by YY1 boosts the course of osteosarcoma through targeting miR-4319/WDR1.Cancer Sci. 2021 Feb;112(2):893-905. doi: 10.1111/cas.14727. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33164271 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular biology of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: translational challenges and clinical perspectives.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jul 5;6(1):249. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00659-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34219130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WDR1 promotes prostate cancer progression through Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Med Oncol. 2024 May 14;41(6):151. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02388-4. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38743149
-
Ubiquitin signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 20;10:1304639. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1304639. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38174069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 maintains c-Myc stability to support pancreatic cancer glycolysis and tumor growth.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 20;22(1):1135. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05962-6. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39707401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deplanque G, Demartines N. Pancreatic cancer: are more chemotherapy and surgery needed? Lancet. 2017;389:985–986. - PubMed
-
- Schlitter AM, Jesinghaus M, Jager C, Konukiewitz B, Muckenhuber A, Demir IE, et al. pT but not pN stage of the 8th TNM classification significantly improves prognostication in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer. 2017;84:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Kleeff J, Michl P. Targeted therapy of pancreatic cancer: biomarkers are needed. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:421–422. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

