Neurological Consequences of 2019-nCoV Infection: A Comprehensive Literature Review
- PMID: 32601577
- PMCID: PMC7317136
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.8790
Neurological Consequences of 2019-nCoV Infection: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Abstract
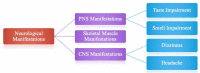
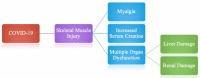
First identified in November 2019 in Hubei Province, the coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 soon spread worldwide to become a global health pandemic. The COVID-19 preferentially damages the respiratory system that produces symptoms such as fever, cough, and shortness of breath. However, the infection often tends to disseminate to involve various organ systems. Recent evidence indicates that SARS-CoV-2 can cause significant neurological damage and resultant neurological symptoms and complications. Here, we provide a comprehensive and thorough review of original articles, case reports, and case series to delineate the possible mechanisms of nervous system invasion and damage by SARS-CoV-2 and subsequent consequences. We divided the neurological manifestations into three categories: (1) Central Nervous System involvement, (2) Peripheral Nervous System manifestations, and (3) Skeletal Muscle Injury. Headache and dizziness were found to be the most prevalent symptoms followed by impaired consciousness. Among the symptoms indicating peripheral nervous system invasion, anosmia and dysgeusia were commonly reported. Skeletal muscle injury predominantly presents as myalgia. In addition, encephalitis, myelitis, cerebrovascular disease, Guillain-Barre syndrome, and Miller Fischer syndrome were among the commonly noted complications. We also emphasized the association of pre-existing comorbidities with neurological manifestations. The aim of this review is to provide a deeper understanding of the potential neurological implications to help neurologists have a high index of clinical suspicion allowing them to manage the patient appropriately.
Keywords: cerebrovascular injury; covid-19; hypoxic injury; immune-mediated injury; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2020, Azim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Human coronaviruses: what do they cause? van der Hoek L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17944272/ Antivir Ther. 2007;12:651–658. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Pneumonia of unknown cause - China. [May;2020 ];https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-ch... 2020
-
- WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. [May;2020 ];https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re... 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
