SARS-CoV-2 and Streptococcus pneumoniae coinfection as a cause of severe pneumonia in an infant
- PMID: 32602267
- PMCID: PMC7361827
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.24916
SARS-CoV-2 and Streptococcus pneumoniae coinfection as a cause of severe pneumonia in an infant
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
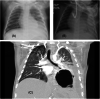
Comment on
-
Multicentre Italian study of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adolescents, preliminary data as at 10 April 2020.Euro Surveill. 2020 May;25(18):2000600. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.18.2000600. Euro Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32400362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanco‐Iglesias E, Oñoro G, Almodovar‐Martín JL, et al. Retrospective study in children with necrotizing pneumonia: nine years of intensive care experience. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39:571‐575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

