The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 32602272
- PMCID: PMC7332325
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0105
The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: To determine the role of diabetes mellitus (DM) in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we explored the clinical characteristics of patients with DM and compared risk factors such as age, glycemic control, and medications to those without DM.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of 117 confirmed patients with COVID-19 which conducted at a tertiary hospital in Daegu, South Korea. The primary outcome was defined as the severe and critical outcome (SCO), of which the composite outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, intensive care unit care, and 28-day mortality. We analyzed what clinical features and glycemic control-related factors affect the prognosis of COVID-19 in the DM group.
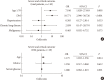
Results: After exclusion, 110 participants were finally included. DM patients (n=29) was older, and showed higher blood pressure compared to non-DM patients. DM group showed higher levels of inflammation-related biomarkers and severity score, and highly progressed to SCO. After adjustment with other risk factors, DM increased the risk of SCO (odds ratio [OR], 10.771; P<0.001). Among the DM patients, SCO was more prevalent in elderly patients of ≥70 years old and age was an independent risk factor for SCO in patients with DM (OR, 1.175; P=0.014), while glycemic control was not. The use of medication did not affect the SCO, but the renin-angiotensin system inhibitors showed protective effects against acute cardiac injury (OR, 0.048; P=0.045).
Conclusion: The COVID-19 patients with DM had higher severity and resulted in SCO. Intensive and aggressive monitoring of COVID-19 clinical outcomes in DM group, especially in elderly patients is warranted.
Keywords: Aged; COVID-19; Diabetes mellitus; Prognosis; Risk factors; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2020 Korean Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Comment in
-
Letter: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405-13).Diabetes Metab J. 2020 Aug;44(4):621-622. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0151. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. PMID: 32856803 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405-13).Diabetes Metab J. 2020 Aug;44(4):625-626. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0167. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. PMID: 32856805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Kornum JB, Thomsen RW, Riis A, Lervang HH, Schonheyder HC, Sorensen HT. Type 2 diabetes and pneumonia outcomes: a population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:2251–2257. - PubMed
-
- McAlister FA, Majumdar SR, Blitz S, Rowe BH, Romney J, Marrie TJ. The relation between hyperglycemia and outcomes in 2,471 patients admitted to the hospital with community-acquired pneumonia. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:810–815. - PubMed

