Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 32602278
- PMCID: PMC7801759
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0190
Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
Background: Metformin is widely marketed medication for the treatment of diabetes, but its pharmacological effect on diabetic peripheral neuropathy remains unclear. In this study, the effect of metformin on peripheral nerves in diabetic rats was investigated using diverse neuronal parameters of nerve fibers.
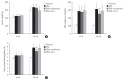
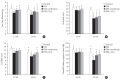
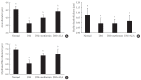
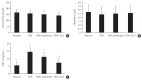
Methods: Rats were assigned to one of four groups (n=7 to 10 per group): normal, diabetes mellitus (DM), DM+metformin (100 mg/kg), and DM+alpha lipoic acid (ALA, 100 mg/kg). DM was induced by streptozotocin/high-fat diet (STZ/HFD). After 12 weeks, the sensory thresholds to mechanical and heat stimuli were assessed. Repeated sensory tests, immunofluorescence microscopic comparison of peripheral nerves, and biochemical blood analysis were performed after 24 weeks.
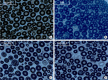
Results: Both DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups showed similar trends to diverse sensory tests at 24 weeks compared to DM group although the degree of change were different according to the stimulated senses. There was no significant difference in the comparison of the intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) of peripheral nerves between the DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups (11.83±0.07 fibers/mm vs. 12.37±1.82 fibers/mm, respectively). Both groups showed preserved IENFD significantly compared with DM group (8.46±1.98 fibers/mm, P<0.05). Sciatic nerve morphology of the experimental animals showed a similar trend to the IENFD, with respect to axonal diameter, myelin sheath thickness, and myelinated fiber diameter.
Conclusion: Metformin has beneficial pharmacological effects on the preservation of peripheral nerves in diabetic rats and its effects are comparable to those of ALA.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Metformin; Peripheral nerves; Thioctic acid; Vitamin B12.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
The Anti-Diabetic Drug Metformin from the Neuropathy Perspective.Diabetes Metab J. 2020 Dec;44(6):840-841. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0252. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. PMID: 33389958 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53).Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Jan;45(1):125-126. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0280. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. PMID: 33508909 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53).Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Jan;45(1):127-128. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0289. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. PMID: 33508910 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tesfaye S. Advances in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2009;3:136–143. - PubMed
-
- Vinik AI, Park TS, Stansberry KB, Pittenger GL. Diabetic neuropathies. Diabetologia. 2000;43:957–973. - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye S, Boulton AJ, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, Lauria G, Malik RA, Spallone V, Vinik A, Bernardi L, Valensi P Toronto Diabetic Neuropathy Expert Group. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:2285–2293. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perry T, Lahiri DK, Chen D, Zhou J, Shaw KT, Egan JM, Greig NH. A novel neurotrophic property of glucagon-like peptide 1: a promoter of nerve growth factor-mediated differentiation in PC12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;300:958–966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

