Multi-Ethnic Genome-Wide Association Study of Decomposed Cardioelectric Phenotypes Illustrates Strategies to Identify and Characterize Evidence of Shared Genetic Effects for Complex Traits
- PMID: 32602732
- PMCID: PMC7520945
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.119.002680
Multi-Ethnic Genome-Wide Association Study of Decomposed Cardioelectric Phenotypes Illustrates Strategies to Identify and Characterize Evidence of Shared Genetic Effects for Complex Traits
Abstract
Background: We examined how expanding electrocardiographic trait genome-wide association studies to include ancestrally diverse populations, prioritize more precise phenotypic measures, and evaluate evidence for shared genetic effects enabled the detection and characterization of loci.
Methods: We decomposed 10 seconds, 12-lead electrocardiograms from 34 668 multi-ethnic participants (15% Black; 30% Hispanic/Latino) into 6 contiguous, physiologically distinct (P wave, PR segment, QRS interval, ST segment, T wave, and TP segment) and 2 composite, conventional (PR interval and QT interval) interval scale traits and conducted multivariable-adjusted, trait-specific univariate genome-wide association studies using 1000-G imputed single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Evidence of shared genetic effects was evaluated by aggregating meta-analyzed univariate results across the 6 continuous electrocardiographic traits using the combined phenotype adaptive sum of powered scores test.
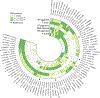
Results: We identified 6 novels (CD36, PITX2, EMB, ZNF592, YPEL2, and BC043580) and 87 known loci (adaptive sum of powered score test P<5×10-9). Lead single-nucleotide polymorphism rs3211938 at CD36 was common in Blacks (minor allele frequency=10%), near monomorphic in European Americans, and had effects on the QT interval and TP segment that ranked among the largest reported to date for common variants. The other 5 novel loci were observed when evaluating the contiguous but not the composite electrocardiographic traits. Combined phenotype testing did not identify novel electrocardiographic loci unapparent using traditional univariate approaches, although this approach did assist with the characterization of known loci.
Conclusions: Despite including one-third as many participants as published electrocardiographic trait genome-wide association studies, our study identified 6 novel loci, emphasizing the importance of ancestral diversity and phenotype resolution in this era of ever-growing genome-wide association studies.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; electrophysiology; epidemiology; genome-wide association study; population.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ancestry-specific associations identified in genome-wide combined-phenotype study of red blood cell traits emphasize benefits of diversity in genomics.BMC Genomics. 2020 Mar 14;21(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6626-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32171239 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study for Resting Electrocardiogram in the Qatari Population Identifies 6 Novel Genes and Validates Novel Polygenic Risk Scores.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Mar 4;14(5):e038341. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.038341. Epub 2025 Feb 26. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40008532 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-mapping, novel loci identification, and SNP association transferability in a genome-wide association study of QRS duration in African Americans.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Oct 1;25(19):4350-4368. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw284. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27577874 Free PMC article.
-
New approaches to disease mapping in admixed populations.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Jun 28;12(8):523-8. doi: 10.1038/nrg3002. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21709689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying functional noncoding variants from genome-wide association studies for cardiovascular disease and related traits.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2015 Apr;26(2):120-6. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000158. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2015. PMID: 25692342 Review.
Cited by
-
Cohort Profile: ZOE 2.0-A Community-Based Genetic Epidemiologic Study of Early Childhood Oral Health.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 1;17(21):8056. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218056. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33139633 Free PMC article.
-
Prioritization of causal genes from genome-wide association studies by Bayesian data integration across loci.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Jan 7;21(1):e1012725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012725. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 39774334 Free PMC article.
-
An adaptive test for meta-analysis of rare variant association studies.Genet Epidemiol. 2020 Jan;44(1):104-116. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22273. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Genet Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 31830326 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Association Study of the Plasma Metabolome Identifies Metabolites Linked to Cardiometabolic Disease in Black Individuals.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 22;13(1):4923. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32275-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35995766 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of biomarker traits in diverse UK biobank participants identify associations missed by European-centric analysis strategies.J Hum Genet. 2022 Feb;67(2):87-93. doi: 10.1038/s10038-021-00968-0. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 34376796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanai M, Akiyama M, Takahashi A, Matoba N, Momozawa Y, Ikeda M, Iwata N, Ikegawa S, Hirata M, Matsuda K, et al. Genetic analysis of quantitative traits in the Japanese population links cell types to complex human diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50:390–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL129982/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007419/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020836/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007416/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HG009840/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101855/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM113134/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL139439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL104608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009080/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111089/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

