Comparison of Mortality Among Participants of Women's Health Initiative Trials With Screening-Detected Breast Cancers vs Interval Breast Cancers
- PMID: 32602908
- PMCID: PMC7327543
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.7227
Comparison of Mortality Among Participants of Women's Health Initiative Trials With Screening-Detected Breast Cancers vs Interval Breast Cancers
Abstract
Importance: Interval breast cancers (IBCs) are cancers that emerge after a mammogram with negative results but before the patient's next scheduled screening. Interval breast cancer has a worse prognosis than cancers detected by screening; however, it is unknown whether the length of the interscreening period is associated with prognostic features and mortality.
Objective: To compare the prognostic features and mortality rate of women with IBCs diagnosed within 1 year or between 1 and 2.5 years of a mammogram with negative results with the prognostic features and mortality rate of women with breast cancers detected by screening.
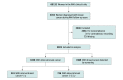
Design, setting, and participants: This cohort study used mammography data, tumor characteristics, and patient demographic data from the Women's Health Initiative study, which recruited participants from 1993 to 1998 and followed up with participants for a median of 19 years. The present study sample for these analyses included women aged 50 to 79 years who participated in the Women's Health Initiative study and includes data collected through March 31, 2018. There were 5455 incidents of breast cancer; only 3019 women compliant with screening were retained in analyses. Statistical analysis was performed from October 25, 2018, to November 24, 2019. Breast cancers detected by screening and IBCs were defined based on mammogram history, date of last mammogram, type of visit, and results of examination. Interval breast cancers were subdivided into those occurring within 1 year or between 1 and 2.5 years after the last protocol-mandated mammogram with negative results.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome of this study was breast cancer-specific mortality for each case of breast cancer detected by screening and IBCs detected within 1 year or between 1 and 2.5 years from a mammogram with negative results. Secondary outcomes included prognostic and tumor characteristics for each group. Comparisons between groups were made using the t test, the χ2 test, and Fine-Gray multivariable cumulative incidence regression analyses.
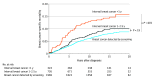
Results: Among the 3019 participants in this analysis, all were women with a mean (SD) age of 63.1 (6.8) years at enrollment and 68.5 (7.1) years at diagnosis. A total of 1050 cases of IBC were identified, with 324 (30.9%) diagnosed within 1 year from a mammogram with negative results and 726 (69.1%) diagnosed between 1 and 2.5 years after last mammogram with negative results. The remaining 1969 cases were breast cancers detected by screening. Interval breast cancers diagnosed within 1 year from a mammogram with negative results had significantly more lobular histologic characteristics (13.0% vs. 8.1%), a larger tumor size (1.97 cm vs 1.43 cm), a higher clinical stage (28.4% vs 17.3% regional and 3.7% vs 0.6% distant), and more lymph node involvement (27.1% vs 17.0%) than cancers detected by screening. Unadjusted breast cancer-specific mortality hazard ratios were significantly higher for IBCs diagnosed within 1 year from a mammogram with negative results compared with breast cancers detected by screening (hazard ratio, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.39-2.65). Higher breast cancer-specific mortality remained statistically significant for IBCs diagnosed within 1 year after adjusting for trial group, molecular subtype, waist to hip ratio, histologic characteristics, and either tumor size (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.03-2.08) or lymph node involvement (hazard ratio, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.03-2.01). However, significance was lost when tumor size and lymph node involvement were both included in the model (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% CI, 0.96-1.88). Interval breast cancers diagnosed between 1 and 2.5 years from a mammogram with negative results were not different from breast cancers detected by screening based on prognostic factors or mortality.
Conclusions and relevance: Women with IBCs diagnosed within 1 year of negative mammogram results overall were associated with worse survival than women with breast cancers detected by screening. These differences in survival may be due to a uniquely aggressive biology among IBC cases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK High-priority evidence gaps for clinical preventive services. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Published November 2018. Accessed May 20, 2020. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/sites/default/files...
-
- Hoff SR, Abrahamsen AL, Samset JH, Vigeland E, Klepp O, Hofvind S. Breast cancer: missed interval and screening-detected cancer at full-field digital mammography and screen-film mammography—results from a retrospective review. Radiology. 2012;264(2):378-386. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12112074 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

