Immunocytochemical Localization of Olfactory-signaling Molecules in Human and Rat Spermatozoa
- PMID: 32603211
- PMCID: PMC7350079
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155420939833
Immunocytochemical Localization of Olfactory-signaling Molecules in Human and Rat Spermatozoa
Abstract
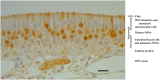
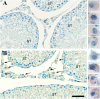
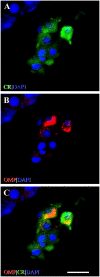
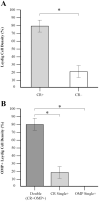
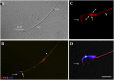
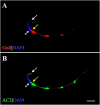
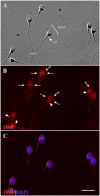
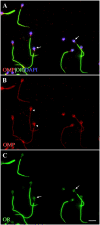
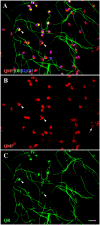
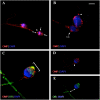
Expression of olfactory receptors (ORs) in non-olfactory tissues has been widely reported over the last 20 years. Olfactory marker protein (OMP) is highly expressed in mature olfactory sensory neurons (mOSNs) of the olfactory epithelium. It is involved in the olfactory signal transduction pathway, which is mediated by well-conserved components, including ORs, olfactory G protein (Golf), and adenylyl cyclase 3 (AC3). OMP is widely expressed in non-olfactory tissues with an apparent preference for motile cells. We hypothesized that OMP is expressed in compartment-specific locations and co-localize with an OR, Golf, and AC3 in rat epididymal and human-ejaculated spermatozoa. We used immunocytochemistry to examine the expression patterns of OMP and OR6B2 (human OR, served as positive olfactory control) in experimentally induced modes of activation and determine whether there are any observable differences in proteins expression during the post-ejaculatory stages of spermatozoal functional maturation. We found that OMP was expressed in compartment-specific locations in human and rat spermatozoa. OMP was co-expressed with Golf and AC3 in rat spermatozoa and with OR6B2 in all three modes of activation (control, activated, and hyperactivated), and the mode of activation changed the co-expression pattern in acrosomal-reacted human spermatozoa. These observations suggest that OMP expression is a reliable indicator of OR-mediated chemoreception, may be used to identify ectopically expressed ORs, and could participate in second messenger signaling cascades that mediate fertility.
Keywords: chemoreception; fluorescence microscopy; interstitial tissue; olfactory epithelium; olfactory marker protein; reproduction; sperm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The functional relevance of olfactory marker protein in the vertebrate olfactory system: a never-ending story.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Jan;383(1):409-427. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03349-9. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33447880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory marker protein expression is an indicator of olfactory receptor-associated events in non-olfactory tissues.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 30;10(1):e0116097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116097. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25635859 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory marker protein regulates prolactin secretion and production by modulating Ca2+ and TRH signaling in lactotrophs.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Apr 6;50(4):1-11. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0035-z. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29622766 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Profiles of Main Olfactory Epithelium in Adenylyl Cyclase 3 Knockout Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 30;16(12):28320-33. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226107. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26633363 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: a neurogenetic matrix.Prog Brain Res. 1991;89:97-122. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61718-5. Prog Brain Res. 1991. PMID: 1839074 Review.
Cited by
-
The functional relevance of olfactory marker protein in the vertebrate olfactory system: a never-ending story.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Jan;383(1):409-427. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03349-9. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33447880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic parameters and genome-wide association studies including the X chromosome for various reproduction and semen quality traits in Nellore cattle.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 10;26(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11193-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39794685 Free PMC article.
-
Odorant and Taste Receptors in Sperm Chemotaxis and Cryopreservation: Roles and Implications in Sperm Capacitation, Motility and Fertility.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 27;12(4):488. doi: 10.3390/genes12040488. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Stallion Spermatozoa, Superoxide Dismutase (Cu-Zn) (SOD1) and the Aldo-Keto-Reductase Family 1 Member b (AKR1B1) Are the Proteins Most Significantly Reduced by Cryopreservation.J Proteome Res. 2021 May 7;20(5):2435-2446. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00932. Epub 2021 Mar 3. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 33656888 Free PMC article.
-
Odorant Receptor OR2C1 Is an Essential Modulator of Boar Sperm Capacitation by Binding with Heparin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 14;24(2):1664. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021664. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buck L, Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991;65(1):175–87. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd G. Discrimination of molecular signals by the olfactory receptor neuron. Neuron. 1994;13(4):771–90. - PubMed
-
- Giorgi F, Maggio R, Bruni L. Are olfactory receptors really olfactive? Biosemiotics. 2011;4(3):331–47.
-
- Buck L. Information coding in the vertebrate olfactory system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19(1):517–44. - PubMed
-
- Malnic B, Hirono J, Sato T, Buck L. Combinatorial receptor codes for odors. Cell. 1999;96(5):713–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

