Stability of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses in the environment and on common touch surfaces and the influence of climatic conditions: A review
- PMID: 32603505
- PMCID: PMC7361302
- DOI: 10.1111/tbed.13707
Stability of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses in the environment and on common touch surfaces and the influence of climatic conditions: A review
Abstract
Although the unprecedented efforts the world has been taking to control the spread of the human coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and its causative aetiology [severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)], the number of confirmed cases has been increasing drastically. Therefore, there is an urgent need for devising more efficient preventive measures, to limit the spread of the infection until an effective treatment or vaccine is available. The preventive measures depend mainly on the understanding of the transmission routes of this virus, its environmental stability, and its persistence on common touch surfaces. Due to the very limited knowledge about SARS-CoV-2, we can speculate its stability in the light of previous studies conducted on other human and animal coronaviruses. In this review, we present the available data on the stability of coronaviruses (CoVs), including SARS-CoV-2, from previous reports to help understand its environmental survival. According to available data, possible airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 has been suggested. SARS-CoV-2 and other human and animal CoVs have remarkably short persistence on copper, latex and surfaces with low porosity as compared to other surfaces like stainless steel, plastics, glass and highly porous fabrics. It has also been reported that SARS-CoV-2 is associated with diarrhoea and that it is shed in the faeces of COVID-19 patients. Some CoVs show persistence in human excrement, sewage and waters for a few days. These findings suggest a possible risk of faecal-oral, foodborne and waterborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in developing countries that often use sewage-polluted waters in irrigation and have poor water treatment systems. CoVs survive longer in the environment at lower temperatures and lower relative humidity. It has been suggested that large numbers of COVID-19 cases are associated with cold and dry climates in temperate regions of the world and that seasonality of the virus spread is suspected.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; animal coronaviruses; common touch surfaces; environmental conditions; fomites; human coronaviruses; inanimate surfaces; persistence; stability; survivability; virus survival.
© 2020 Blackwell Verlag GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
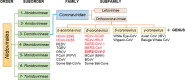
Figures
References
-
- Aboubakr, H. , & Goyal, S. (2019). Involvement of Egyptian Foods in Foodborne Viral Illnesses: The Burden on Public Health and Related Environmental Risk Factors: An Overview. Food and Environmental Virology, 11, 315–339. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, C. , Goede, D. P. , Morrison, R. B. , Davies, P. R. , Rovira, A. , Marthaler, D. G. , & Torremorell, M. (2014). Evidence of infectivity of airborne porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and detection of airborne viral RNA at long distances from infected herds. Veterinary Research, 45(1), 73. 10.1186/s13567-014-0073-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araujo, M. B. , & Naimi, B. (2020). Spread of SARS‐CoV‐2 Coronavirus likely to be constrained by climate. medRxiv. 10.1101/2020.03.12.20034728 - DOI
-
- Bäcker, A. (2020). Follow the Sun: Slower COVID‐19 Morbidity and Mortality Growth at Higher Irradiances. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3567587 or doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3567587. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

