Towards a Secure Thermal-Energy Aware Routing Protocol in Wireless Body Area Network Based on Blockchain Technology
- PMID: 32604851
- PMCID: PMC7349352
- DOI: 10.3390/s20123604
Towards a Secure Thermal-Energy Aware Routing Protocol in Wireless Body Area Network Based on Blockchain Technology
Abstract
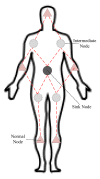
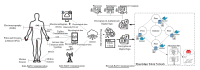
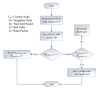
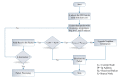
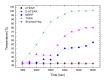
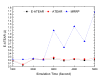
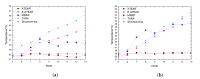
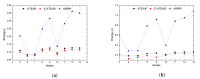
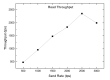
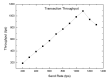
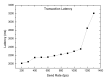
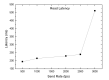
The emergence of biomedical sensor devices, wireless communication, and innovation in other technologies for healthcare applications result in the evolution of a new area of research that is termed as Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs). WBAN originates from Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), which are used for implementing many healthcare systems integrated with networks and wireless devices to ensure remote healthcare monitoring. WBAN is a network of wearable devices implanted in or on the human body. The main aim of WBAN is to collect the human vital signs/physiological data (like ECG, body temperature, EMG, glucose level, etc.) round-the-clock from patients that demand secure, optimal and efficient routing techniques. The efficient, secure, and reliable designing of routing protocol is a difficult task in WBAN due to its diverse characteristic and restraints, such as energy consumption and temperature-rise of implanted sensors. The two significant constraints, overheating of nodes and energy efficiency must be taken into account while designing a reliable blockchain-enabled WBAN routing protocol. The purpose of this study is to achieve stability and efficiency in the routing of WBAN through managing temperature and energy limitations. Moreover, the blockchain provides security, transparency, and lightweight solution for the interoperability of physiological data with other medical personnel in the healthcare ecosystem. In this research work, the blockchain-based Adaptive Thermal-/Energy-Aware Routing (ATEAR) protocol for WBAN is proposed. Temperature rise, energy consumption, and throughput are the evaluation metrics considered to analyze the performance of ATEAR for data transmission. In contrast, transaction throughput, latency, and resource utilization are used to investigate the outcome of the blockchain system. Hyperledger Caliper, a benchmarking tool, is used to evaluate the performance of the blockchain system in terms of CPU utilization, memory, and memory utilization. The results show that by preserving residual energy and avoiding overheated nodes as forwarders, high throughput is achieved with the ultimate increase of the network lifetime. Castalia, a simulation tool, is used to evaluate the performance of the proposed protocol, and its comparison is made with Multipath Ring Routing Protocol (MRRP), thermal-aware routing algorithm (TARA), and Shortest-Hop (SHR). Evaluation results illustrate that the proposed protocol performs significantly better in balancing of temperature (to avoid damaging heat effect on the body tissues) and energy consumption (to prevent the replacement of battery and to increase the embedded sensor node life) with efficient data transmission achieving a high throughput value.
Keywords: blockchain; implanted sensors; internet of things; smart contract; thermal/energy-aware routing protocol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Blockchain Based Delay and Energy Harvest Aware Healthcare Monitoring System in WBAN Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 2;22(15):5763. doi: 10.3390/s22155763. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35957320 Free PMC article.
-
Designing Transmission Strategies for Enhancing Communications in Medical IoT Using Markov Decision Process.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Dec 15;18(12):4450. doi: 10.3390/s18124450. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30558343 Free PMC article.
-
An Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol for Reliable Data Transmission in Wireless Body Area Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 29;19(19):4238. doi: 10.3390/s19194238. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31569568 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Routing Protocols in WBAN for Healthcare Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Apr 5;19(7):1638. doi: 10.3390/s19071638. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30959817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy Efficiency and Reliability Considerations in Wireless Body Area Networks: A Survey.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jan 17;2022:1090131. doi: 10.1155/2022/1090131. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9897817. doi: 10.1155/2023/9897817. PMID: 35082909 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of Blockchain, IoT and Machine Learning for Multistage Quality Control and Enhancing Security in Smart Manufacturing.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 20;21(4):1467. doi: 10.3390/s21041467. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672464 Free PMC article.
-
Smart Contracts and Shared Platforms in Sustainable Health Care: Systematic Review.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Jan 31;13:e58575. doi: 10.2196/58575. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 39889283 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Blockchain in the Medical Field: Narrative Review.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Oct 28;23(10):e28613. doi: 10.2196/28613. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34533470 Free PMC article.
-
Early Life Stress Detection Using Physiological Signals and Machine Learning Pipelines.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;12(1):91. doi: 10.3390/biology12010091. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671783 Free PMC article.
-
Technological Requirements and Challenges in Wireless Body Area Networks for Health Monitoring: A Comprehensive Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 6;22(9):3539. doi: 10.3390/s22093539. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35591234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jamil F., Hang L., Kim K., Kim D. A Novel Medical Blockchain Model for Drug Supply Chain Integrity Management in a Smart Hospital. Electronics. 2019;8:505. doi: 10.3390/electronics8050505. - DOI
-
- Qadri R., Faiq M.A. Fresh Water Pollution Dynamics and Remediation. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2020. Freshwater Pollution: Effects on Aquatic Life and Human Health; pp. 15–26.
-
- Hasan K., Biswas K., Ahmed K., Nafi N.S., Islam M.S. A comprehensive review of wireless body area network. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019;143:178–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2019.06.016. - DOI
-
- Baig M.M. Ph.D. Thesis. Auckland University of Technology; Auckland, New Zealand: 2014. Smart Vital Signs Monitoring and Novel Falls Prediction System for Older Adults.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

