Multi-Scale Surface Treatments of Titanium Implants for Rapid Osseointegration: A Review
- PMID: 32604854
- PMCID: PMC7353126
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10061244
Multi-Scale Surface Treatments of Titanium Implants for Rapid Osseointegration: A Review
Abstract
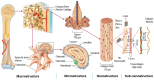
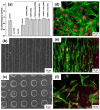
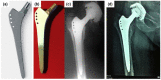
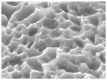
The propose of this review was to summarize the advances in multi-scale surface technology of titanium implants to accelerate the osseointegration process. The several multi-scaled methods used for improving wettability, roughness, and bioactivity of implant surfaces are reviewed. In addition, macro-scale methods (e.g., 3D printing (3DP) and laser surface texturing (LST)), micro-scale (e.g., grit-blasting, acid-etching, and Sand-blasted, Large-grit, and Acid-etching (SLA)) and nano-scale methods (e.g., plasma-spraying and anodization) are also discussed, and these surfaces are known to have favorable properties in clinical applications. Functionalized coatings with organic and non-organic loadings suggest good prospects for the future of modern biotechnology. Nevertheless, because of high cost and low clinical validation, these partial coatings have not been commercially available so far. A large number of in vitro and in vivo investigations are necessary in order to obtain in-depth exploration about the efficiency of functional implant surfaces. The prospective titanium implants should possess the optimum chemistry, bionic characteristics, and standardized modern topographies to achieve rapid osseointegration.
Keywords: macro-scale; micro-scale; nano-scale; rapid bone integration; roughness; surface modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Xiao L., Wu S., Liu B., Yang H., Yang L. Advances in metallic biomaterials with both osteogenic and anti-infection properties. ACTA Metall. Sin. 2017;53:1284–1302.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

