Genetic Markers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis: A Review
- PMID: 32604993
- PMCID: PMC7369725
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21134569
Genetic Markers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis: A Review
Abstract
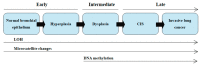
Lung cancer is the most often diagnosed cancer in the world and the most frequent cause of cancer death. The prognosis for lung cancer is relatively poor and 75% of patients are diagnosed at its advanced stage. The currently used diagnostic tools are not sensitive enough and do not enable diagnosis at the early stage of the disease. Therefore, searching for new methods of early and accurate diagnosis of lung cancer is crucial for its effective treatment. Lung cancer is the result of multistage carcinogenesis with gradually increasing genetic and epigenetic changes. Screening for the characteristic genetic markers could enable the diagnosis of lung cancer at its early stage. The aim of this review was the summarization of both the preclinical and clinical approaches in the genetic diagnostics of lung cancer. The advancement of molecular strategies and analytic platforms makes it possible to analyze the genome changes leading to cancer development-i.e., the potential biomarkers of lung cancer. In the reviewed studies, the diagnostic values of microsatellite changes, DNA hypermethylation, and p53 and KRAS gene mutations, as well as microRNAs expression, have been analyzed as potential genetic markers. It seems that microRNAs and their expression profiles have the greatest diagnostic potential value in lung cancer diagnosis, but their quantification requires standardization.
Keywords: NGS; carcinogenesis; epigenetic markers; genetic alterations; genetic markers; liquid biopsy; lung cancer; microRNA; molecular heterogeneity; molecular landscape.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The significance of epigenetic alterations in lung carcinogenesis.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jan;40(1):309-25. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2063-4. Epub 2012 Oct 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23086271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers along the continuum of care in lung cancer.Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2016;245:S40-5. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2016.1208446. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2016. PMID: 27542002 Review.
-
DNA methylation and nonsmall cell lung cancer.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011 Nov;294(11):1787-95. doi: 10.1002/ar.21471. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21956844 Review.
-
Lung cancer epigenetics and genetics.Int J Cancer. 2008 Jul 1;123(1):1-7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23605. Int J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18425819 Review.
-
A Novel Epigenetic Signature for Early Diagnosis in Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;22(13):3361-71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2346. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26842235
Cited by
-
Upregulation of nuclear division cycle 80 contributes to therapeutic resistance via the promotion of autophagy-related protein-7-dependent autophagy in lung cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 29;13:985601. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.985601. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36105209 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic circ-SLC16A1 promotes progression of non-small cell lung cancer via regulation of the miR-1287-5p/profilin 2 axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Mar 27;29(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00549-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38539084 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of S-Palmitoylation in Cancer Stem Cells of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 21;9:734897. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.734897. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34621750 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Functional Roles of MicroRNAs in the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 7;21(21):8362. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218362. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33171811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of microRNAs in Lung Cancer: Mechanisms, Diagnostics and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 15;26(8):3736. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083736. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous