TOP mRNPs: Molecular Mechanisms and Principles of Regulation
- PMID: 32605040
- PMCID: PMC7407576
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10070969
TOP mRNPs: Molecular Mechanisms and Principles of Regulation
Abstract
The cellular response to changes in the surrounding environment and to stress requires the coregulation of gene networks aiming to conserve energy and resources. This is often achieved by downregulating protein synthesis. The 5' Terminal OligoPyrimidine (5' TOP) motif-containing mRNAs, which encode proteins that are essential for protein synthesis, are the primary targets of translational control under stress. The TOP motif is a cis-regulatory RNA element that begins directly after the m7G cap structure and contains the hallmark invariant 5'-cytidine followed by an uninterrupted tract of 4-15 pyrimidines. Regulation of translation via the TOP motif coordinates global protein synthesis with simultaneous co-expression of the protein components required for ribosome biogenesis. In this review, we discuss architecture of TOP mRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complexes, the principles of their assembly, and the modes of regulation of TOP mRNA translation.
Keywords: 5’ Terminal Oligopyrimidine; LARP1; RNA; RNA binding proteins; translation regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
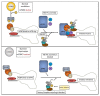
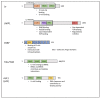
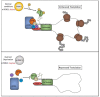

References
-
- Wek S.A., Zhu S., Wek R.C. The histidyl-tRNA synthetase-related sequence in the eIF-2 alpha protein kinase GCN2 interacts with tRNA and is required for activation in response to starvation for different amino acids. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995;15:4497–4506. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.8.4497. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

