Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance
- PMID: 32605310
- PMCID: PMC7400347
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10070438
Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance
Abstract
Paratyphoid fever is caused by the bacterium Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi (A, B and C), and contributes significantly to global disease burden. One of the major challenges in the diagnosis of paratyphoid fever is the lack of a proper gold standard. Given the absence of a licensed vaccine against S. Paratyphi, this diagnostic gap leads to inappropriate antibiotics use, thus, enhancing antimicrobial resistance. In addition, the symptoms of paratyphoid overlap with other infections, including the closely related typhoid fever. Since the development and utilization of a standard, sensitive, and accurate diagnostic method is essential in controlling any disease, this review discusses a new promising approach to aid the diagnosis of paratyphoid fever. This advocated approach is based on the use of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor and DNA probes to detect specific nucleic acid sequences of S. Paratyphi. We believe that this SPR-based genoassay can be a potent alternative to the current conventional diagnostic methods, and could become a rapid diagnostic tool for paratyphoid fever.
Keywords: SPR; Salmonella Paratyphi; bacterial detection; biosensor; optical sensor; paratyphoid fever.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


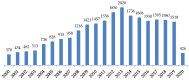

References
-
- Morse S.A., Mietzner T.A., Miller S., Riedel S. Jawetz Melnick & Adelbergs Medical Microbiology 28 E. McGraw-Hill Education; New York, NY, USA: 2019.
-
- Grimont P.A., Weill F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars. WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella; Paris, France: 2007. pp. 1–166.
-
- Centers-for-Disease-Control-and-Prevention Serotypes and the Importance of Serotyping Salmonella. [(accessed on 16 April 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/reportspubs/salmonella-atlas/serotyping-i....
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

