Electrochemical Evaluation of a Multi-Site Clinical Depth Recording Electrode for Monitoring Cerebral Tissue Oxygen
- PMID: 32605324
- PMCID: PMC7407998
- DOI: 10.3390/mi11070632
Electrochemical Evaluation of a Multi-Site Clinical Depth Recording Electrode for Monitoring Cerebral Tissue Oxygen
Abstract
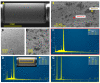
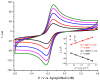
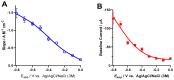
The intracranial measurement of local cerebral tissue oxygen levels-PbtO2-has become a useful tool for the critical care unit to investigate severe trauma and ischemia injury in patients. Our preliminary work in animal models supports the hypothesis that multi-site depth electrode recording of PbtO2 may give surgeons and critical care providers needed information about brain viability and the capacity for better recovery. Here, we present a surface morphology characterization and an electrochemical evaluation of the analytical properties toward oxygen detection of an FDA-approved, commercially available, clinical grade depth recording electrode comprising 12 Pt recording contacts. We found that the surface of the recording sites is composed of a thin film of smooth Pt and that the electrochemical behavior evaluated by cyclic voltammetry in acidic and neutral electrolyte is typical of polycrystalline Pt surface. The smoothness of the Pt surface was further corroborated by determination of the electrochemical active surface, confirming a roughness factor of 0.9. At an optimal working potential of -0.6 V vs. Ag/AgCl, the sensor displayed suitable values of sensitivity and limit of detection for in vivo PbtO2 measurements. Based on the reported catalytical properties of Pt toward the electroreduction reaction of O2, we propose that these probes could be repurposed for multisite monitoring of PbtO2 in vivo in the human brain.
Keywords: brain tissue oxygen; in vivo monitoring; multi-site clinical depth electrode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lang E.W., Jaeger M. Systematic and comprehensive literature review of publications on direct cerebral oxygenation monitoring. Open Crit. Care Med. J. 2013;6:1–24. doi: 10.2174/1874828701306010001. - DOI
-
- Bohman L.E., Pisapia J.M., Sanborn M.R., Frangos S., Lin E., Kumar M., Park S., Kofke W.A., Stiefel M.F., Leroux P.D., et al. Response of brain oxygen to therapy correlates with long-term outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care. 2013;19:320–328. doi: 10.1007/s12028-013-9890-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stiefel M.F., Spiotta A., Gracias V.H., Garuffe A.M., Guillamondegui O., Maloney-Wilensky E., Bloom S., Grady M.S., LeRoux P.D. Reduced mortality rate in patients with severe traumatic brain injury treated with brain tissue oxygen monitoring. J. Neurosurg. 2005;103:805–811. doi: 10.3171/jns.2005.103.5.0805. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

