Real-World Assessment of the Impact of Erectile Dysfunction on Sexual Planning Behavior and Health- and Treatment-Related Outcomes Among Men in 8 Countries
- PMID: 32605816
- PMCID: PMC7471092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esxm.2020.05.001
Real-World Assessment of the Impact of Erectile Dysfunction on Sexual Planning Behavior and Health- and Treatment-Related Outcomes Among Men in 8 Countries
Abstract
Introduction: The effect of erectile dysfunction (ED) on sexual planning behaviors and outcomes in men taking phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is) is not well studied.
Aims: To assess sexual habits, behaviors, and treatment-related outcomes of PDE5I-treated men with ED.
Methods: This cross-sectional observational study recruited men aged 30 to 70 years with mild-to-severe ED from 8 diverse countries (the United States, the United Kingdom, Italy, Russia, Turkey, Israel, China, and Japan) to complete an approximately 15-minute survey. Differences were evaluated using bivariate analyses, and data were summarized using descriptive statistics.
Main outcome measures: Self-reported data were collected for demographics, health characteristics, treatment, sexual habits, ED severity, ED-specific quality of life, and treatment satisfaction.
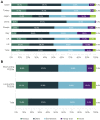
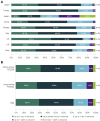
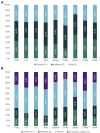
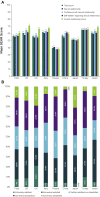
Results: The survey was completed by 1,575 men. Mean frequency of sexual intercourse was 5.7 times/month. Overall, 87.1% of men always, often, or sometimes planned for sexual activity. Of those planning in advance, 32.8% and 40.6% agreed or strongly agreed that they plan for specific days of the week and times of day, respectively. Sexual planning habits were similar for patients taking short-acting vs long-acting PDE5Is. The most commonly cited reasons for planning sexual activity were needing time to take medication (48.4%), needing to make sure medication has taken effect (43.4%), convenient time for sexual activity (34.9%), and needing the partner's agreement (33.4%). Mean Self-Esteem and Relationship Questionnaire total score was 56.4.
Conclusions: The differences in ED burden and sexual planning behavior observed across countries were not influenced by the type of PDE5I being taken, suggesting that cultural differences are an important factor when considering types of ED treatment. These findings provide a better understanding of burden, sexual habits, planning behaviors, quality of life, and treatment-related outcomes among PDE5I-treated men with ED in 8 Western and non-Western countries and may aid healthcare providers in selecting optimal treatments. Goldstein I, Giraldi A, Maculaitis MC, Real-World Assessment of the Impact of Erectile Dysfunction on Sexual Planning Behavior and Health- and Treatment-Related Outcomes Among Men in 8 Countries. J Sex Med 2020;8:338-349.
Keywords: Erectile Dysfunction; Global Male Sexual Habits Survey; Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors; Quality of Life; Sexual Activity Planning.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sexual habits of men with ED who take phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors: a survey conducted in 7 countries.Int J Clin Pract. 2018 Apr;72(4):e13074. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.13074. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Int J Clin Pract. 2018. PMID: 29460994 Free PMC article.
-
Degree of Planning of Sexual Intercourse Among Men From China, Japan, and Taiwan Taking Medication for Erectile Dysfunction: Findings of an Observational, Cross-Sectional Survey.Sex Med. 2019 Mar;7(1):54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Sex Med. 2019. PMID: 30522975 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a first treatment with phosphodiesterase inhibitors on men and partners' quality of sexual life: results of a prospective study in primary care.J Sex Med. 2013 Jul;10(7):1850-60. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12186. Epub 2013 May 16. J Sex Med. 2013. PMID: 23679019
-
Erectile function and assessments of erection hardness correlate positively with measures of emotional well-being, sexual satisfaction, and treatment satisfaction in men with erectile dysfunction treated with sildenafil citrate (Viagra).Urology. 2006 Sep;68(3 Suppl):26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.06.027. Urology. 2006. PMID: 17011373 Review.
-
Update on the Safety of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction.Sex Med Rev. 2018 Apr;6(2):242-252. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.08.001. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Sex Med Rev. 2018. PMID: 28923561 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors as treatment for erectile dysfunction: a webinar-based poll unveiling perceptions of healthcare professionals.J Comp Eff Res. 2024 Jul;13(7):e230155. doi: 10.57264/cer-2023-0155. Epub 2024 May 22. J Comp Eff Res. 2024. PMID: 38775343 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, Comorbidities, and Risk Factors of Erectile Dysfunction: Results from a Prospective Real-World Study in the United Kingdom.Int J Clin Pract. 2022 Mar 20;2022:5229702. doi: 10.1155/2022/5229702. eCollection 2022. Int J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35693549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lue T.F., Giuliano F., Montorsi F. Summary of the recommendations on sexual dysfunctions in men. J Sex Med. 2004;1:6–23. - PubMed
-
- Sand M.S., Fisher W., Rosen R. Erectile dysfunction and constructs of masculinity and quality of life in the multinational Men's Attitudes to Life Events and Sexuality (MALES) study. J Sex Med. 2008;5:583–594. - PubMed
-
- McCabe M.P., Sharlip I.D., Lewis R. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a consensus statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:144–152. - PubMed
-
- Rosen R.C., Fisher W.A., Eardley I. The multinational Men's Attitudes to Life Events and Sexuality (MALES) study: I. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and related health concerns in the general population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004;20:607–617. - PubMed
-
- McCabe M.P., Sharlip I.D., Lewis R. Risk factors for sexual dysfunction among women and men: a consensus statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:153–167. - PubMed

