Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance and pH Monitoring: A Step Towards Pediatric Reference Values
- PMID: 32606258
- PMCID: PMC7329155
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm19205
Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance and pH Monitoring: A Step Towards Pediatric Reference Values
Abstract
Background/aims: Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring (MII/pH) is considered the most accurate test to detect gastroesophageal reflux (GER), however lacking reference values. We aim to determine reference values for the pediatric population and to correlate these values with age and postprandial/fasting period.
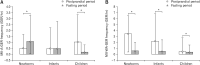
Methods: We evaluated MII/pH traces from patients (newborns, infants, and children) admitted to 3 Italian hospitals and who underwent MII/ pH for suspected GER disease. Patients with MII/pH traces that showed significant symptom-reflux associations and/or a pathological reflux index (> 6% for newborns and infants, > 3% for children) were excluded. Traces were analysed in their entirety, and in the postprandial period (first hour after a meal) and the fasting period (the following hours before the next meal) separately.
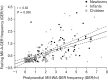
Results: A total of 195 patients (46 newborns, 83 infants, and 66 children) were included. Age positively correlated with frequency of acidic GER events (r = 0.37, P < 0.05) and negatively associated with weakly acidic GER events (r = 0.46, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: This study describes the distribution of MII/pH values in a pediatric population with normally acidic GER exposure and no significant association between GER events and symptoms. These MII/pH values may be used as reference values in clinical practice for a corrected GER disease diagnosis in the pediatric population.
Keywords: Child; Esophageal pH monitoring; Gastroesophageal reflux; Infant; Reference values.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
24 h combined esophageal multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring in children with chronic cough.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Aug 22;24(1):538. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04975-w. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39174910 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Symptomatic Young Infants Using Multichannel Intraluminal pH-Impedance Testing: A large Cohort Study from a Single Center.Am J Perinatol. 2025 Mar;42(4):486-494. doi: 10.1055/a-2405-1545. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Am J Perinatol. 2025. PMID: 39209301
-
Addition of pH-impedance monitoring to standard pH monitoring increases the yield of symptom association analysis in infants and children with gastroesophageal reflux.J Pediatr. 2009 Feb;154(2):248-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.08.019. Epub 2008 Sep 27. J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 18823910
-
Standard protocol devised by the Japanese Pediatric Impedance Working Group for combined multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH measurements in children.Surg Today. 2020 Jul;50(7):664-671. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01833-6. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Surg Today. 2020. PMID: 31214780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reflux monitoring in children.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Oct;28(10):1452-9. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12922. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016. PMID: 27682990 Review.
Cited by
-
Oesophageal pH-Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Validation of General Population Reference Values in Children with Chronic Neurological Impairments.J Clin Med. 2021 Jul 29;10(15):3351. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153351. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34362132 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring values in children with cerebral palsy: A comparative multicenter study.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025 Jul;81(1):125-130. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.70058. Epub 2025 May 6. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40329476 Free PMC article.
-
Editing Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-pH Tracings to Reduce Non-reflux-related Esophageal Acidification.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024 Jan 30;30(1):121-122. doi: 10.5056/jnm23164. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024. PMID: 38173165 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multichannel intraesophageal impedance with pH metry in Saudi children.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 1;30(2):103-107. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_249_23. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 37997390 Free PMC article.
-
24 h combined esophageal multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring in children with chronic cough.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Aug 22;24(1):538. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04975-w. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39174910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vandenplas Y, Rudolph CD, Di Lorenzo C, et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;49:498–547. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181b7f563. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

