Efficacy and Safety of VisuEvo® and Cationorm® for the Treatment of Evaporative and Non-Evaporative Dry Eye Disease: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Cross-Over, Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 32606580
- PMCID: PMC7308118
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S258081
Efficacy and Safety of VisuEvo® and Cationorm® for the Treatment of Evaporative and Non-Evaporative Dry Eye Disease: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Cross-Over, Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the efficacy of the new lubricating product VisuEvo® (VSE) vs Cationorm® (CTN) in patients with dry eye disease (DED).
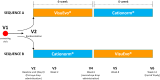
Methods: Seventy-two patients with evaporative (n=54) and non-evaporative DED (n=18) were included in a multicenter, double-blind, 12-week cross-over study to receive VSE (6 weeks) and CTN (6 weeks) in randomized sequence. After baseline, two visits were performed during each period (intermediate and final visit, respectively at 2 and 6 weeks from the beginning of each period). Primary (tear break-up time, TBUT) and secondary endpoints (Schirmer I, Ferning, blink rate, osmometry, cytokine and lipid expression, ocular surface staining, patient satisfaction, and OSDI score) were compared.
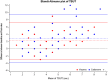
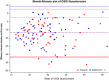
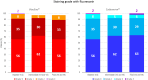
Results: Sixty-three patients were evaluated for efficacy and 68 patients for safety. The intergroup differences for mean TBUT values were not significant at any study visit (baseline 3.2 ±1.5 sec; intermediate visits 4.5 ± 1.9 and 4.5 ± 1.8 sec in VSE and CTN groups, respectively, p = 0.10; final visits 5.4 ± 2.4 and 6.0 ± 3.1, respectively, p=0.63). Also, the assessment of secondary endpoints showed no significant difference between the two groups. The two study treatments were equally effective in evaporative and non-evaporative DED. The safety profile was excellent for both ocular treatments; transient blurred vision was observed in 11 patients only during CTN, 10 patients only during VSE, and 16 during both treatments.
Conclusion: VSE was non-inferior to CTN in restoring tear film composition, increasing its stability and reducing ocular surface damage in evaporative and non-evaporative DED patients.
Study identifier: NCT03833882.
Keywords: Ocular Surface Disease Index questionnaire; evaporative dry eye disease; glaucoma; meibomian gland disturbance; ocular surface; tear break-up time.
© 2020 Fogagnolo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Paolo Fogagnolo and Luca Rossetti received honoraria for medical meetings and advisory board from Visufarma S.p.A, Rome, Italy. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Craig JP, Nichols KK, Akpek E, et al. TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report. Ocul Surf. 2017;15(3):276e83. - PubMed

