Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Endothelial Dysfunctional Properties of Nano-Selenium in vitro and in vivo of Hyperhomocysteinemic Rats
- PMID: 32606691
- PMCID: PMC7320884
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S255392
Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Endothelial Dysfunctional Properties of Nano-Selenium in vitro and in vivo of Hyperhomocysteinemic Rats
Abstract
Purpose: Elevation of blood homocysteine (Hcy) level (hyperhomocysteinemia) is a risk factor for cardiovascular disorders and is closely associated with endothelial dysfunction. The present study aims to investigate the protective effect and underlying mechanism of nanoscale selenium (Nano-Se) in Hcy-mediated vascular endothelial cell dysfunction in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and methods: By incubating vascular endothelial cells with exogenous Hcy and generating hyperhomocysteinemic rat model, the effects of Nano-Se on hyperhomocysteinemia-mediated endothelial dysfunction and its essential mechanisms were investigated.
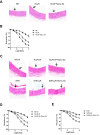
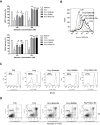
Results: Nano-Se inhibited Hcy-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis by preventing the downregulation of glutathione peroxidase enzyme 1 and 4 (GPX1, GPX4) in the vascular endothelial cells, thus effectively prevented the vascular damage in vitro and in vivo in the hyperhomocysteinemic rats. Nano-Se possessed similar protective effects but lower toxicity against Hcy in vascular endothelial cells when compared with other forms of Se.
Conclusion: The application of Nano-Se could serve as a novel promising strategy against Hcy-mediated vascular dysfunction with reduced risk of Se toxicity.
Keywords: GPXs; Nano-Se; ROS; endothelium dysfunction; glutathione peroxidase enzymes; homocysteine; nano-selenium; reactive oxygen species.
© 2020 Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Sieber F, Daziano JP, Gunther WH, et al. Elemental selenium generated by the photobleaching of selenomerocyanine photosensitizers forms conjugates with serum macromolecules that are toxic to tumor cells. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem. 2005;180(3–4):647–657. doi: 10.1080/10426500590907200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

