The Effect of CYP2C9 Genotype Variants in Type 2 Diabetes on the Pharmacological Effectiveness of Sulfonylureas, Diabetic Retinopathy, and Nephropathy
- PMID: 32606720
- PMCID: PMC7308133
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S230639
The Effect of CYP2C9 Genotype Variants in Type 2 Diabetes on the Pharmacological Effectiveness of Sulfonylureas, Diabetic Retinopathy, and Nephropathy
Abstract
Aim: Type 2 diabetes (T2D), as a major cause of morbidity and mortality, is predicted to have a prevalence of 629 million by 2045. As diabetic patients show considerable inter-individual variation in response to antidiabetic treatment, this study aimed to investigate the gene polymorphism of cytochrome P450 as well as the effectiveness and safety of glibenclamide and gliclazide for different genotypes of CYP2C9. Besides, the chronic side effects of T2D including retinal microvasculature complications or retinopathy and renal dysfunction due to nephropathy in different genotypes were considered.
Patients and methods: The participants including 80 T2D patients treated with glibenclamide or gliclazide were recruited from university hospitals of Ahvaz Jundishpur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, in the southwest of Iran. Blood samples were collected from the patients at 2.5h after the morning dose of glibenclamide and 12h after the last dose of gliclazide. Genotyping from the extracted DNA was, then, performed using PCR-RFLP. The plasma level of glibenclamide and gliclazide was, in turn, measured by the reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography.
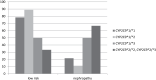
Results: The results showed that the wild-type allele, i.e., CYP2C9*1, occurred in the highest frequency (0.8), while the frequency rates of the mutant allele, i.e., CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3, were 0.15 and 0.05, respectively. Moreover, no significant association was found between any of the genotypes as well as the clinical and biochemical characteristics of the patients. The findings also showed that the plasma level of sulfonylureas (i.e., glibenclamide and gliclazide) was the highest in the patients with the CYP2C9*3 allele. It was also found that 75.9% of the patients with variant genotypes had experienced hypoglycemia events. Furthermore, in the absence of wild type allele, a significant increase was observed in retinopathy (p=0.039) and nephropathy (p=0.05).
Conclusion: The findings can provide guidelines for the optimal management of the treatment protocols with sulfonylurea intended to control the T2D complications.
Keywords: CYP2C9; glibenclamide; gliclazide; nephropathy; retinopathy.
© 2020 Saberi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms on response to glibenclamide in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;67(8):797-801. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1013-8. Epub 2011 Feb 20. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21336994
-
CYP2C9*3 gene variant contributes independently to glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with glibenclamide.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2018 Dec;43(6):768-774. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12710. Epub 2018 May 26. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2018. PMID: 29802808
-
CYP2C93 variant is associated with antidiabetes efficacy of gliclazide in Chinese type 2 diabetes patients.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Sep;7(5):764-8. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12486. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27181593 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of efficacy, secondary failure rate, and complications of sulfonylureas.J Diabetes Complications. 1994 Oct-Dec;8(4):201-3. doi: 10.1016/1056-8727(94)90044-2. J Diabetes Complications. 1994. PMID: 7833494 Review.
-
Evaluating gliclazide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2022 Dec;23(17):1869-1877. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2022.2141108. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36300277 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of gliclazide for different genotypes of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19.Arch Pharm Res. 2025 Mar;48(3):234-250. doi: 10.1007/s12272-024-01528-8. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Arch Pharm Res. 2025. PMID: 39760829
-
Association of CYP2C9*2 Allele with Sulphonylurea-Induced Hypoglycaemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Pharmacogenetic Study in Pakistani Pashtun Population.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 16;11(8):2282. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082282. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626778 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenomics of sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes mellitus; a systematic review.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021 Dec 1;21(1):863-879. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00908-x. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 35673432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Federation ID, editor. IDF Diabetes Atlas Update Poster. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 20152015.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials