Hsa_circRNA_000166 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Regulating miR-330-5p/ELK1 in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 32606768
- PMCID: PMC7297456
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S243795
Hsa_circRNA_000166 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Regulating miR-330-5p/ELK1 in Colon Cancer
Retraction in
-
Hsa_circRNA_000166 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Regulating miR-330-5p/ELK1 in Colon Cancer [Retraction].Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Apr 3;17:285-286. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S471178. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38586814 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a novel class of non-coding RNAs, which are widely expressed in human cells, have essential roles in the development and progression of cancers. The aim of this study is to figure out the role of circ_000166 in colon cancer (CC) development and the signaling pathway involved.
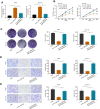
Materials and methods: HT29 and HCT116 cells were transfected with siRNA of circRNA, miRNA mimics and inhibitors. Cell proliferation, migration and invasion were examined using CCK-8 assay and transwell assay, respectively. Luciferase reporter assay was used to validate the targets of circRNA and miRNA. CC cells were implanted into nude mice subcutaneously to detect tumor growth.
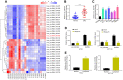
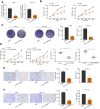
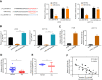
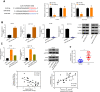
Results: hsa_circRNA_000166 was significantly upregulated in the human CC tissue and in the CC cell lines. Knockdown of hsa_circRNA_000166 reduced cell viability, colony formation, migration and invasion in vitro and decreased tumor size and weight in vivo. Luciferase reporter assay revealed that miR-330-5p was the target of circRNA_000166. miR-330-5p could bind to 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of ELK1 to downregulate both mRNA and protein expression of ELK1. Dual inhibition of circRNA_000166 and miR-330-5p inhibited the suppression of cell proliferation, migration and invasion induced by si-circRNA_000166.
Conclusion: The data of this study demonstrated that the hsa_circRNA_000166 could upregulated the expression of gene ELK1 by sponging miR-330-5p, which may contribute to a better understanding of the regulatory circRNA/miRNA/mRNA network and CC pathogenesis.
Keywords: ELK1; circRNA_000166; colon cancer; miRNA-330-5p.
© 2020 Zhao and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

