Role of Dopaminergic Receptors Within the Ventral Tegmental Area in Antinociception Induced by Chemical Stimulation of the Lateral Hypothalamus in an Animal Model of Orofacial Pain
- PMID: 32606911
- PMCID: PMC7304680
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S255250
Role of Dopaminergic Receptors Within the Ventral Tegmental Area in Antinociception Induced by Chemical Stimulation of the Lateral Hypothalamus in an Animal Model of Orofacial Pain
Abstract
Introduction: The ventral tegmental area (VTA), as one of the classical components of the brain reward circuitry, shares large neural networks with the pain processing system. We previously showed the role of VTA dopamine receptors in modulation of lateral hypothalamus (LH)-induced antinociception in acute pain conditions. However, considering the fact that the neural systems involved in the mediation of tonic pain are not the same as those that mediate phasic pain. In the present study, we aimed to examine the role of intra-VTA dopamine receptors in LH-induced antinociceptive responses during tonic orofacial pain conditions.
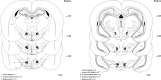
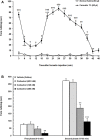
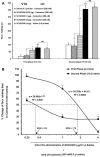
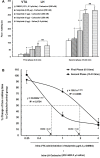
Methods: Male Wistar rats weighing 230-250 g were implanted with two separate cannulae into the LH and VTA on the same side. Different solutions of carbachol (62.5, 125 and 250 nM), as a non-selective cholinergic receptor agonist that activates the LH projecting neurons, were microinjected into the LH. In the other groups, D1-like dopamine receptor antagonist, SCH-23390 (0.25, 1 and 4 µg/03 µL saline) or D2-like dopamine receptor antagonist, Sulpiride (0.25, 1 and 4 µg/0.3 µL DMSO 12%) were microinjected into VTA, 5 min prior intra-LH carbachol (250 nM), then subjected to orofacial formalin test. Intra-LH carbachol microinjection dose-dependently attenuated biphasic orofacial pain.
Results: Intra-VTA administration of SCH-23390 or Sulpiride dose-dependently decreased intra-LH carbachol-induced antinociception during both phases of orofacial formalin test with further effects in the late phase.
Discussion: The findings suggest that chemical stimulation of the LH by carbachol possibly activates the orexin projecting neurons and subsequently, the VTA dopaminergic neurons involved in the orofacial pain modulation. Detecting such neural circuitry offers an alternative approach in the development of more efficient therapies for such debilitating pain conditions.
Keywords: D1-like dopamine receptor; D2-like dopamine receptor; lateral hypothalamus; orofacial formalin test; pain; ventral tegmental area.
© 2020 Matini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The contribution of orexin receptors within the ventral tegmental area to modulation of antinociception induced by chemical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus in the animal model of orofacial pain in the rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;31(5):500-509. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000531. Behav Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31895063
-
Role of D1- and D2-like dopaminergic receptors in the nucleus accumbens in modulation of formalin-induced orofacial pain: Involvement of lateral hypothalamus.Physiol Behav. 2018 May 1;188:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.01.020. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Physiol Behav. 2018. PMID: 29421337
-
Dopaminergic receptors in the ventral tegmental area modulated the lateral hypothalamic stimulation-induced antinociception in an animal model of tonic pain.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Apr 23;751:135827. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135827. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33727128
-
Role of dopamine D2-like receptors within the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens in antinociception induced by lateral hypothalamus stimulation.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Oct 1;292:508-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26166189
-
Converging circuits between pain and depression: the ventral tegmental area as a therapeutic hub.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 2;14:1278023. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1278023. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37849731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
D1 receptor-expressing neurons in ventral tegmental area alleviate mouse anxiety-like behaviors via glutamatergic projection to lateral septum.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Feb;28(2):625-638. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01809-y. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36195641 Free PMC article.
-
Looking for a Beam of Light to Heal Chronic Pain.J Pain Res. 2024 Mar 16;17:1091-1105. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S455549. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38510563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Roles of the D1- and D2-Like Dopamine Receptors Within the Ventral Tegmental Area in Modulating the Antinociception Induced by Forced Swim Stress in the Rat.Neurochem Res. 2024 Jan;49(1):143-156. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04017-4. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37642894
-
Neuroanatomical Basis for the Orexinergic Modulation of Anesthesia Arousal and Pain Control.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 26;16:891631. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.891631. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35558876 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-Brain Crosstalk and the Central Mechanisms of Orofacial Pain.Brain Sci. 2023 Oct 13;13(10):1456. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13101456. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37891825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

