Electroacupuncture Regulates Pain Transition by Inhibiting the mGluR5-PKCε Signaling Pathway in the Dorsal Root Ganglia
- PMID: 32606913
- PMCID: PMC7311359
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S251948
Electroacupuncture Regulates Pain Transition by Inhibiting the mGluR5-PKCε Signaling Pathway in the Dorsal Root Ganglia
Abstract
Background: Acute pain can transition to chronic pain, presenting a major clinical challenge. Electroacupuncture (EA) can partly prevent the transition from acute to chronic pain. However, little is known about the mechanisms underlying the effect of EA. This study investigated the effect of EA on pain transition and the activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5)-protein kinase C epsilon (PKCε) signaling pathway in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG).
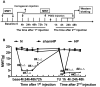
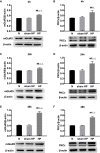
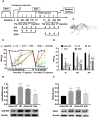
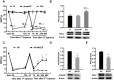
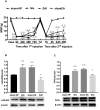
Methods: The hyperalgesic priming model was established by the sequential intraplantar injection of carrageenan (1%, 100 μL) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) into the left hind paw of rats. EA treatment (2/100 Hz, 30 min, once/day) was applied at bilateral Zusanli (ST36) and Kunlun (BL60) acupoints in rats. Von Frey filaments were used to investigate the mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) at different time points. The protein expression levels of mGluR5 and PKCε in the ipsilateral L4-L6 DRGs of rats were detected by Western blot. Some pharmacological experiments were performed to evaluate the relationship between mGluR5, PKCε and the MWT. It was also used to test the effects of EA on the expression levels of mGluR5 and PKCε and changes in the MWT.
Results: Sequential injection of carrageenan and PGE2 significantly decreased the MWT of rats and up-regulated the expression level of mGluR5 and PKCε in the ipsilateral L4-L6 DRGs. EA can reverse the hyperalgesic priming induced by sequential injection of carrageenan/PGE and down-regulate the protein expression of mGluR5 and PKCε. Glutamate injection instead of PGE2 can mimic the hyperalgesic priming model. Pharmacological blocking of mGluR5 with specific antagonist MTEP can prevent the hyperalgesic priming and inhibit the activation of PKCε in DRGs. Furthermore, EA also produced analgesic effect on the hyperalgesic priming rats induced by carrageenan/mGluR5 injection and inhibited the high expression of PKCε. Sham EA produced none analgesic and regulatory effect.
Conclusion: EA can regulate pain transition and it may relate with its inhibitory effect on the activation of mGluR5-PKCε signaling pathway in the DRGs.
Keywords: DRGs; PKCε; electroacupuncture; hyperalgesic priming; mGluR5; pain transition.
© 2020 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Electroacupuncture on Pain Transition and Content of Protein Kinase Cε in Dorsal Root Ganglia in Hyperalgesia Rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Nov 25;43(11):677-81. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180212. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 30585462 Chinese.
-
Role of GABAAR in the Transition From Acute to Chronic Pain and the Analgesic Effect of Electroacupuncture on Hyperalgesic Priming Model Rats.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 17;15:691455. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.691455. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34220444 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Regulates Pain Transition Through Inhibiting PKCε and TRPV1 Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglion.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jul 20;15:685715. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.685715. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34354561 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Mechanisms in Managing Preoperative Anxiety and Postoperative Pain Chronification: A Review.J Pain Res. 2024 Dec 4;17:4089-4100. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S498373. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39650212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperalgesic Priming in the Transition From Acute to Chronic Pain: Focus on Different Models and the Molecular Mechanisms Involved.J Pain Res. 2025 Mar 21;18:1491-1501. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S514851. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 40135188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Involvement of Glutamate-mGluR5 Signaling in the Development of Vulvar Hypersensitivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 9;26(2):523. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020523. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859236 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal root ganglia P2X4 and P2X7 receptors contribute to diabetes-induced hyperalgesia and the downregulation of electroacupuncture on P2X4 and P2X7.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):29-41. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09844-8. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35218450 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate Alleviates Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice by Decreasing Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Activity and Neuroinflammation in Primary Sensory Neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 May 27;15:902572. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.902572. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35694442 Free PMC article.
-
Strong Twirling-Rotating Manual Acupuncture with 4 r/s Is Superior to 2 r/s in Relieving Pain by Activating C-Fibers in Rat Models of CFA-Induced Pain.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 12;2021:5528780. doi: 10.1155/2021/5528780. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34675986 Free PMC article.
-
EA participates in pain transition through regulating KCC2 expression by BDNF-TrkB in the spinal cord dorsal horn of male rats.Neurobiol Pain. 2023 Jan 5;13:100115. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100115. eCollection 2023 Jan-Jul. Neurobiol Pain. 2023. PMID: 36875547 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

