CCNY Accelerates Cylcin E Expression to Regulate the Proliferation of Laryngeal Carcinoma Cells via MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 32606977
- PMCID: PMC7320751
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S241620
CCNY Accelerates Cylcin E Expression to Regulate the Proliferation of Laryngeal Carcinoma Cells via MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: Laryngeal carcinoma is a common cancer among head and neck tumors, accounting for 0.5-1% new cancer cases or deaths of all tumors throughout the body. Despite improvements in diagnostic and therapy, the prognosis of laryngeal carcinoma patients still remains poor. Thus, it is very important to identify the biomarkers involved in the molecular pathogenesis of laryngeal carcinoma. Cyclin Y (CCNY) is a conserved cell cycle regulator that acts as a growth factor in many cancers. The clinical significance of CCNY in laryngeal carcinoma remains unknown. The function of CCNY in laryngocarcinoma was studied in this paper.
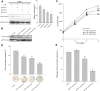
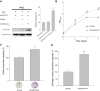
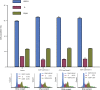
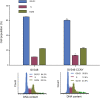
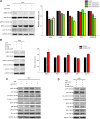
Materials and methods: CCNY knock-out cells were constructed by CRISPR/CAS9 technique. CCNY overexpression cells were also constructed based on CCNY knock-out cells. Cell growth ability was detected by MTS assay, high-content cell analysis, colony formation assays, and anchorage-independent growth assays. The protein levels in laryngocarcinoma cells were determined by Western blot. The role of CCNY in cell cycle progression was evaluated by flow cytometry.
Results: CCNY knock-out cells and CCNY up-regulation cell models were obtained successfully. Suppression of CCNY expression inhibited Hep2 cell growth. Cell growth was enhanced by the up-regulation of CCNY. The percentage of cells in G1 phase was altered when CCNY expression was down-regulated or up-regulated. The phosphorylation level of MEK and ERK as well as cyclin E protein level was also regulated by the expression level of CCNY.
Conclusion: In laryngocarcinoma cell line Hep2 cells, cell proliferation was controlled by CCNY. The expression of CCNY was involved in the cell cycle progress of Hep2 cells. It indicated that CCNY could promote cell growth by activating MEK/ERK/cyclin E signaling pathway.
Keywords: CCNY; ERK; cell cycle; cyclin E; laryngocarcinoma.
© 2020 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

