Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy and Safety of a Plasma-Derived VWF/FVIII Concentrate (Formulation V) in Pediatric Patients with von Willebrand Disease (SWIFTLY-VWD Study)
- PMID: 32607039
- PMCID: PMC7319533
- DOI: 10.2147/JBM.S236789
Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy and Safety of a Plasma-Derived VWF/FVIII Concentrate (Formulation V) in Pediatric Patients with von Willebrand Disease (SWIFTLY-VWD Study)
Abstract
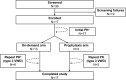
Purpose: Formulation V (VONCENTO®) is a plasma-derived high-concentration/low-volume, high-purity von Willebrand factor (VWF)/factor VIII (FVIII) concentrate, originally indicated for von Willebrand disease (VWD) in adults and adolescents. This multicenter, open-label study (SWIFTLY-VWD) evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK), as well as hemostatic efficacy and safety, of Formulation V in pediatric patients (<12 years) with severe VWD requiring treatment or prophylaxis of bleedings.
Methods: PK investigations were performed following one dose of Formulation V at Day 1 and 180. Nonsurgical bleeds were analyzed, while hemostatic efficacy was graded as excellent/good/moderate/none. Safety assessments included adverse events, and presence of VWF and/or FVIII inhibitors.
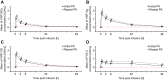
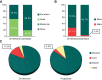
Results: Formulation V was administered as on-demand (N=13) or prophylaxis therapy (N=4) for 12 months (<6 years, N=9; 6 to <12 years, N=8). PK parameters for VWF markers were generally comparable to adults but showed lower VWF:ristocetin cofactor (RCo) exposure. Incidence of major bleeds was lower for prophylaxis (3.3%) than on-demand therapy (27.1%); joint bleeds were also lower (3.3% vs 11.5%, respectively). Investigator-reported excellent/good hemostatic efficacy against nonsurgical bleeds was 100%. No clinically relevant differences in PK, hemostatic efficacy, or safety were observed between age-groups (<6 years and 6 to <12 years). Formulation V was well tolerated. Adverse events were mild-moderate and consistent with the adult safety profile. No cases of anaphylactic reactions or angioedema, development of FVIII/VWF inhibitors, thromboembolic events, or viral infections were reported.
Conclusion: This study provides evidence for use of Formulation V to treat and prevent bleeding in pediatric patients with severe VWD, and led to the European approval of Formulation V in children.
Keywords: clinical trial; pediatrics; prophylaxis; von Willebrand disease; von Willebrand factor-factor VIII concentrate.
© 2020 Auerswald et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GA has received reimbursements for attending symposia/congresses and/or honoraria for speaking and/or consulting and/or funds for research support from CSL Behring. OS has received honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Takeda, and CSL Behring, and declares membership of speaker bureaus for Novo Nordisk, Takeda and Pfizer. WS and TR are employees of CSL Behring. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety of Plasma-Derived von Willebrand Factor/Factor VIII Concentrate (Voncento) in von Willebrand Disease.Thromb Haemost. 2024 Sep;124(9):828-841. doi: 10.1055/a-2253-9701. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 38272065 Free PMC article.
-
An Open-Label Extension Study to Assess the Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of a Plasma-Derived von Willebrand Factor (VWF)/Factor VIII (FVIII) Concentrate in Patients with von Willebrand Disease (SWIFT-VWDext Study).J Blood Med. 2020 Oct 9;11:345-356. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S268907. eCollection 2020. J Blood Med. 2020. PMID: 33117020 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, Safety and Pharmacokinetic Results of a Phase III, Open-Label, Multicenter Study with a Plasma-Derived Von Willebrand Factor (VWF)/Factor VIII (FVIII) Concentrate in Pediatric Patients <12 Years of Age with Hemophilia A (SWIFTLY-HA Study).J Blood Med. 2021 Jun 21;12:483-495. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S299130. eCollection 2021. J Blood Med. 2021. PMID: 34188580 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety of a plasma-derived VWF/FVIII concentrate (VONCENTO) for on-demand and prophylactic treatment in patients with von Willebrand disease (SWIFT-VWD study).Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2017 Mar;28(2):152-162. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000568. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2017. PMID: 27203734 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous DDAVP and factor VIII-von Willebrand factor concentrate for the treatment and prophylaxis of bleedings in patients With von Willebrand disease type 1, 2 and 3.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2007 Jan;13(1):14-34. doi: 10.1177/1076029606296399. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2007. PMID: 17164493 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of long-term prophylaxis using pdFVIII/VWF concentrate in patients with inherited von Willebrand disease.Eur J Haematol. 2022 Jul;109(1):109-117. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13778. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Eur J Haematol. 2022. PMID: 35438801 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety of Plasma-Derived von Willebrand Factor/Factor VIII Concentrate (Voncento) in von Willebrand Disease.Thromb Haemost. 2024 Sep;124(9):828-841. doi: 10.1055/a-2253-9701. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 38272065 Free PMC article.
-
An Open-Label Extension Study to Assess the Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of a Plasma-Derived von Willebrand Factor (VWF)/Factor VIII (FVIII) Concentrate in Patients with von Willebrand Disease (SWIFT-VWDext Study).J Blood Med. 2020 Oct 9;11:345-356. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S268907. eCollection 2020. J Blood Med. 2020. PMID: 33117020 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of plasma-derived von Willebrand factor/factor VIII concentrate (wilate) prophylaxis in children and adolescents with von Willebrand disease - WIL-31 study post hoc analysis.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2025 Feb 28;9(2):102719. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2025.102719. eCollection 2025 Feb. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2025. PMID: 40224272 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic management of patients with von Willebrand disease.Ther Adv Hematol. 2021 Dec 22;12:20406207211064064. doi: 10.1177/20406207211064064. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34987743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flood VH, Montgomery RR. von Willebrand disease: biologic diagnosis In: Lee CA, Berntorp EE, Hoots WK, editors. Textbook of Hemophilia. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010:294–301.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

