Essential Oils and Health
- PMID: 32607090
- PMCID: PMC7309671
Essential Oils and Health
Abstract
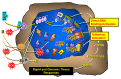
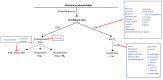
Essential oils (EOs) have risen in popularity over the past decade. These oils function in society as holistic integrative modalities to traditional medicinal treatments, where many Americans substitute EOs in place of other prescribed medications. EOs are found in a multitude of products including food flavoring, soaps, lotions, shampoos, hair styling products, cologne, laundry detergents, and even insect repellents. EOs are complex substances comprised of hundreds of components that can vary greatly in their composition depending upon the extraction process by the producer or the origin of the plant. Thus, making it difficult to determine which pathways in the body are affected. Here, we review the published research that shows the health benefits of EOs as well as some of their adverse effects. In doing so, we show that EOs, as well as some of their individual components, possess antimicrobial, antiviral, antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties as well as purported psychogenic effects such as relieving stress, treating depression, and aiding with insomnia. Not only do we show the health benefits of using EOs, but we also indicate risks associated with their use such as their endocrine disrupting properties leading to the induction of premature breast growth in young adolescents. Taken together, there are many positive and potentially negative risks to human health associated with EOs, which make it important to bring awareness to all their known effects on the human body.
Keywords: Endocrine disruptors; anti-inflammatory; antimicrobial; gynecomastia; prepubertal; psychological.
Copyright ©2020, Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine. This work is written in part by US Government employees and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
References
-
- Essential Oils Market Size , Share & Trends Analysis Report By Application (Cleaning & Home, Medical, Food & Beverages, Spa & Relaxation), By Product, By Sales Channel, And Segment Forecasts, 2019 - 2025. Grand View Research; 2019.
-
- Ali B, Al-Wabel NA, Shams S, Ahamad A, Khan SA, Anwar F. Essential oils used in aromatherapy. Syst Rev. 2015:601–11.
-
- Svoboda KP, Deans SG. Biological Activities of Essential Oils from Selected Aromatic Plants. 1995: International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), Leuven, Belgium; 10.17660/ActaHortic.1995.390.28 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
