Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Hengyang, Hunan Province, China
- PMID: 32607332
- PMCID: PMC7322431
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2554
Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Hengyang, Hunan Province, China
Abstract
Background: In December 2019, an ongoing outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first identified in Wuhan, China. The characteristics of COVID-19 patients treated in local hospitals in Wuhan are not fully representative of patients outside Wuhan. Therefore, it is highly essential to analyze the epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in areas outside Wuhan or Hubei Province. To date, a limited number of studies have concentrated on the epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with different genders, clinical classification, and with or without basic diseases.
Aim: To study the epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Hengyang (China) and provide a reliable reference for the prevention and control of COVID-19.
Methods: From January 16 to March 2, 2020, a total of 48 confirmed cases of COVID-19 were reported in Hengyang, and those cases were included in this study. The diagnostic criteria, clinical classification, and discharge standard related to COVID-19 were in line with the Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 7) released by National Health Commission and National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 in pharyngeal swab specimens was detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. All the data were imported into the excel worksheet and statistically analyzed by using SPSS 25.0 software.
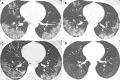
Results: A total of 48 cases of COVID-19 were collected, of which 1 was mild, 38 were moderate, and 9 were severe. It was unveiled that there were 31 (64.6%) male patients and 17 (35.4%) female patients, with a female-to-male ratio of 1.82:1. The range of age of patients with COVID-19 was dominantly 30-49 years old [25 (52.1%) of 48], followed by those aged over 60 years old [11 (22.9%)]. Besides, 29.2% (14 of 48) of patients had basic diseases, and 57.2% (8 of 14) of patients with basic diseases were aged over 60 years old. The occupations of 48 COVID-19 patients were mainly farmers working in agricultural production [15 (31.5%) of 48], rural migrant workers from Hengyang to Wuhan [15 (31.5%)], and service workers operating in the service sector [8 (16.7%)]. The mean latent period was 6.86 ± 3.57 d, and the median was 7 [interquartile range (IQR): 4-9] d. The mean time from onset of symptoms to the first physician visit was 3.38 ± 2.98 (95%CI: 2.58-9.18) d, with a median of 2 (IQR: 1-5) d, and the mean time from hospital admission to confirmed diagnosis was 2.29 ± 2.11 (95%CI: 1.18-6.42) d, with a median of 2 (IQR: 1-3) d. The main symptoms were fever [43 (89.6%) of 48], cough and expectoration [41 (85.4%)], fatigue [22 (45.8%)], and chills [22 (45.8%)]. Other symptoms included poor appetite [13 (27.1%)], sore throat [9 (18.8%)], dyspnea [9 (18.8%)], diarrhea [7 (14.6%)], dizziness [5 (10.4%)], headache [5 (10.4%)], muscle pain [5 (10.4%)], nausea and vomiting [4 (8.3%)], hemoptysis [4 (8.3%)], and runny nose [1 (2.1%)]. The numbers of peripheral blood leukocytes, lymphocytes, and eosinophils were significantly reduced in the majority of the patients. The levels of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, blood glucose, lactate dehydrogenase, D-dimer, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), myoglobin (MB), and creatine kinase (CK) were increased in 64.6%, 44.7%, 43.2%, 37.0%, 29.5%, 22.9%,20.8%, 21.6%, 13.6%, and 12.8% of patients, respectively. The incidence of ALT elevation in male patients was remarkably higher than that in females (P < 0.01), while the incidences of AST, CK, and blood glucose elevations in severe patients were remarkably higher than those in moderate patients (P < 0.05, respectively). Except for the mild patients, chest computed tomography showed characteristic pulmonary lesions. All the patients received antiviral drugs, 38 (79.2%) accepted traditional Chinese medicine, and 2 (4.2%) received treatment of human umbilical-cord mesenchymal stem cells. On March 2, 2020, 48 patients with COVID-19 were all cured and discharged.
Conclusion: Based on our results, patients with COVID-19 often have multiple organ dysfunction or damage. The incidences of ALT elevation in males, and AST, CK, and blood glucose elevations in severe patients are remarkably higher.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019; Epidemiology; Hengyang; Novel coronavirus pneumonia; SARS-CoV-2.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical and Immune Features of Hospitalized Pediatric Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Jun 1;3(6):e2010895. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.10895. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32492165 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severity of COVID-19 outside Wuhan: a double-center retrospective cohort study of 213 cases in Hunan, China.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020 Jan-Dec;14:1753466620963035. doi: 10.1177/1753466620963035. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020. PMID: 33138694 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of clinical features in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 for severe disease.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 May 28;45(5):536-541. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2020.200384. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32879103 Chinese, English.
-
Clinical Symptom Differences Between Mild and Severe COVID-19 Patients in China: A Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2021 Jan 14;8:561264. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.561264. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33520906 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Cases During the Early Phase of COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jun 11;7:295. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00295. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32596248 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neurological complications of coronavirus infection; a comparative review and lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic.J Neurol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;417:117085. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.117085. Epub 2020 Aug 7. J Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32871412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D-dimer, disease severity, and deaths (3D-study) in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 100 studies.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 8;11(1):21888. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01462-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34750495 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Possible Significance of ACE2 in the Human Liver, Esophagus, Stomach, and Colon.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 25;2021:6949902. doi: 10.1155/2021/6949902. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9879323. doi: 10.1155/2023/9879323. PMID: 34484401 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Evaluation of nutritional status and health behaviors of patients infected with COVID-19.J Family Med Prim Care. 2021 Sep;10(9):3459-3463. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_181_21. Epub 2021 Sep 30. J Family Med Prim Care. 2021. PMID: 34760773 Free PMC article.
-
The incubation period of COVID-19: a global meta-analysis of 53 studies and a Chinese observation study of 11 545 patients.Infect Dis Poverty. 2021 Sep 17;10(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00901-9. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021. PMID: 34535192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

