Membrane cholesterol dependence of cannabinoid modulation of glycine receptor
- PMID: 32608538
- PMCID: PMC8147113
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201903093R
Membrane cholesterol dependence of cannabinoid modulation of glycine receptor
Abstract
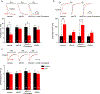
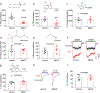
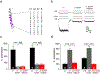
Cannabinoids exert therapeutic effects on several diseases such as chronic pain and startle disease by targeting glycine receptors (GlyRs). Our previous studies have shown that cannabinoids target a serine residue at position 296 in the third transmembrane helix of the α1/α3 GlyR. This site is located on the outside of the ion channel protein at the lipid interface where the cholesterol concentrates. However, whether membrane cholesterol regulates cannabinoid-GlyR interaction remains unknown. Here, we show that GlyRs are closely associated with cholesterol/caveolin-rich domains at subcellular levels. Membrane cholesterol reduction significantly inhibits cannabinoid potentiation of glycine-activated currents in cultured spinal neurons and in HEK 293T cells expressing α1/α3 GlyRs. Such inhibition is fully rescued by cholesterol replenishment in a concentration-dependent manner. Molecular docking calculations further reveal that cholesterol regulates cannabinoid enhancement of GlyR function through both direct and indirect mechanisms. Taken together, these findings suggest that cholesterol is critical for the cannabinoid-GlyR interaction in the cell membrane.
Keywords: cannabinoid; cholesterol; glycine receptor.
© 2020 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures

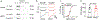
References
-
- Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, and Rasenick MM (2006) Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 8, 128–140 - PubMed
-
- Sooksawate T, and Simmonds MA (2001) Effects of membrane cholesterol on the sensitivity of the GABA(A) receptor to GABA in acutely dissociated rat hippocampal neurones. Neuropharmacology 40, 178–184 - PubMed
-
- Barrantes FJ (2007) Cholesterol effects on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Neurochem 103 Suppl 1, 72–80 - PubMed
-
- Frank C, Giammarioli AM, Pepponi R, Fiorentini C, and Rufini S. (2004) Cholesterol perturbing agents inhibit NMDA-dependent calcium influx in rat hippocampal primary culture. FEBS letters 566, 25–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

