Renin and Survival in Patients Given Angiotensin II for Catecholamine-Resistant Vasodilatory Shock. A Clinical Trial
- PMID: 32609011
- PMCID: PMC7605187
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201911-2172OC
Renin and Survival in Patients Given Angiotensin II for Catecholamine-Resistant Vasodilatory Shock. A Clinical Trial
Abstract
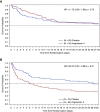
Rationale: Exogenous angiotensin II increases mean arterial pressure in patients with catecholamine-resistant vasodilatory shock (CRVS). We hypothesized that renin concentrations may identify patients most likely to benefit from such therapy.Objectives: To test the kinetic changes in renin concentrations and their prognostic value in patients with CRVS.Methods: We analyzed serum samples from patients enrolled in the ATHOS-3 (Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock) trial for renin, angiotensin I, and angiotensin II concentrations before the start of administration of angiotensin II or placebo and after 3 hours.Measurements and Main Results: Baseline serum renin concentration (normal range, 2.13-58.78 pg/ml) was above the upper limits of normal in 194 of 255 (76%) study patients with a median renin concentration of 172.7 pg/ml (interquartile range [IQR], 60.7 to 440.6 pg/ml), approximately threefold higher than the upper limit of normal. Renin concentrations correlated positively with angiotensin I/II ratios (r = 0.39; P < 0.001). At 3 hours after initiation of angiotensin II therapy, there was a 54.3% reduction (IQR, 37.9% to 66.5% reduction) in renin concentration compared with a 14.1% reduction (IQR, 37.6% reduction to 5.1% increase) with placebo (P < 0.0001). In patients with renin concentrations above the study population median, angiotensin II significantly reduced 28-day mortality to 28 of 55 (50.9%) patients compared with 51 of 73 patients (69.9%) treated with placebo (unstratified hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.35 to 0.88; P = 0.012) (P = 0.048 for the interaction).Conclusions: The serum renin concentration is markedly elevated in CRVS and may identify patients for whom treatment with angiotensin II has a beneficial effect on clinical outcomes.Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT02338843).
Keywords: angiotensin I; angiotensin-converting enzyme defect; distributive shock; renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system.
Figures


Comment in
-
Renin, Angiotensin II, and the Journey to Evidence-based Individual Treatment Effects.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Nov 1;202(9):1209-1211. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202007-2731ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32749864 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alteration of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Shock: Role of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Feb 15;203(4):526-527. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202010-3873LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33152252 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Picod et al.: Alteration of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Shock: Role of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Feb 15;203(4):527-528. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202010-3968LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33152253 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock. 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017;45:486–552. - PubMed
-
- Khanna A, English SW, Wang XS, Ham K, Tumlin J, Szerlip H, et al. ATHOS-3 Investigators. Angiotensin II for the treatment of vasodilatory shock. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:419–430. - PubMed

