Ultrasonography of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid arteries: B-mode imaging
- PMID: 32609972
- PMCID: PMC7418858
- DOI: 10.15557/JoU.2020.0022
Ultrasonography of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid arteries: B-mode imaging
Abstract
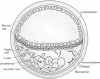
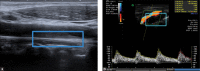
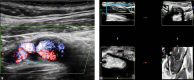
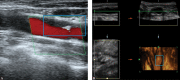
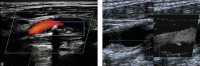
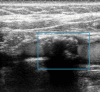
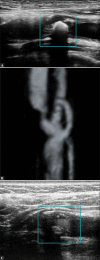
The most common type of stroke, i.e. ischemic stroke, is a great challenge for contemporary medicine as it poses both diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties. Atherosclerosis, which is rapidly beginning to affect more and more social groups, is the main cause of cerebrovascular accidents. Atherosclerosis is currently defined as a generalized, dynamic and heterogeneous inflammatory and immune process affecting arterial walls. Atherosclerotic plaque is the emanation of this disease. As the paradigm of the diagnosis of atherosclerosis has changed, it has become crucial to properly identify plaque instability within the carotid arteries by evaluating parameters and phenomena that signify a developing cascade of complications, eventually leading to stroke. Irrespective of the ultrasound technique employed, proper morphological evaluation of atherosclerotic plaque, involving observation of its echogenicity, i.e. subjective analysis of its structure, with the classification to Gray-Weale-Nicolaides types as well as assessment of the integrity of its surface, makes it possible to roughly evaluate plaque morphology and thereby its stability. This enables treatment planning and therapy monitoring. This evaluation should be a prelude to further diagnostic work-up, which involves non-invasive examinations that enable unambiguous assessment of plaque stability. These examinations include contrast-enhanced ultrasound to assess progression or recession of inflammation, which presents as plaque neovascularization, or shear wave elastography to objectively define tissue stiffness, and thereby its mineralization.
The most common type of stroke, i.e. ischemic stroke, is a great challenge for contemporary medicine as it poses both diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties. Atherosclerosis, which is rapidly beginning to affect more and more social groups, is the main cause of cerebrovascular accidents. Atherosclerosis is currently defined as a generalized, dynamic and heterogeneous inflammatory and immune process affecting arterial walls. Atherosclerotic plaque is the emanation of this disease. As the paradigm of the diagnosis of atherosclerosis has changed, it has become crucial to properly identify plaque instability within the carotid arteries by evaluating parameters and phenomena that signify a developing cascade of complications, eventually leading to stroke. Irrespective of the ultrasound technique employed, proper morphological evaluation of atherosclerotic plaque, involving observation of its echogenicity, i.e. subjective analysis of its structure, with the classification to Gray-Weale–Nicolaides types as well as assessment of the integrity of its surface, makes it possible to roughly evaluate plaque morphology and thereby its stability. This enables treatment planning and therapy monitoring. This evaluation should be a prelude to further diagnostic work-up, which involves non-invasive examinations that enable unambiguous assessment of plaque stability. These examinations include contrast-enhanced ultrasound to assess progression or recession of inflammation, which presents as plaque neovascularization, or shear wave elastography to objectively define tissue stiffness, and thereby its mineralization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



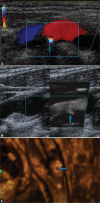
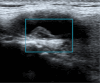

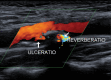
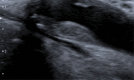
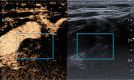
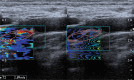
References
-
- Grabowska-Fudala B, Jaracz K, Górna K: Zapadalność, śmiertelność i umieralność z powodu udarów mózgu – aktualne tendencje i prognozy na przyszłość. Przegl Emidemiol 2010; 64: 439–442. - PubMed
-
- The World Health Organization MONICA Project (monitoring trends and determinants in cardiovascular disease): a major international collaboration WHO MONICA Project Principal Investigators. J Clin Epidemiol 1988; 41: 105–114. - PubMed
-
- de Bray JM: Consensus concerning the morphology and the risk of carotid plaques. Cerebrovasc Dis 1997; 7: 289–296.
-
- Li J, Mi D, Pu Y, Zou X, Pan Y, Soo Y et al. : Comparison of carotid atherosclerotic plaque characteristics between patients with first-time and recurrent acute ischaemic stroke using B-mode ultrasound. Neurol Res 2015: 1–5. - PubMed
-
- Nyman E, Vanoli D, Näslund U, Grönlund C: Inter-sonographer reproducibility of carotid ultrasound plaque detection using Mannheim consensus in subclinical atherosclerosis. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2020; 40: 46–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
