Poly-arginine-18 (R18) Confers Neuroprotection through Glutamate Receptor Modulation, Intracellular Calcium Reduction, and Preservation of Mitochondrial Function
- PMID: 32610439
- PMCID: PMC7412265
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25132977
Poly-arginine-18 (R18) Confers Neuroprotection through Glutamate Receptor Modulation, Intracellular Calcium Reduction, and Preservation of Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
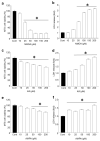
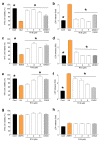
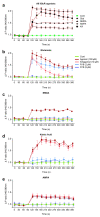
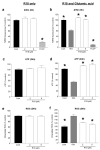
Recent studies have highlighted that a novel class of neuroprotective peptide, known as cationic arginine-rich peptides (CARPs), have intrinsic neuroprotective properties and are particularly effective anti-excitotoxic agents. As such, the present study investigated the mechanisms underlying the anti-excitotoxic properties of CARPs, using poly-arginine-18 (R18; 18-mer of arginine) as a representative peptide. Cortical neuronal cultures subjected to glutamic acid excitotoxicity were used to assess the effects of R18 on ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR)-mediated intracellular calcium influx, and its ability to reduce neuronal injury from raised intracellular calcium levels after inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum calcium uptake by thapsigargin. The results indicate that R18 significantly reduces calcium influx by suppressing iGluR overactivation, and results in preservation of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and ATP production, and reduced ROS generation. R18 also protected cortical neurons against thapsigargin-induced neurotoxicity, which indicates that the peptide helps maintain neuronal survival when intracellular calcium levels are elevated. Taken together, these findings provide important insight into the mechanisms of action of R18, supporting its potential application as a neuroprotective therapeutic for acute and chronic neurological disorders.
Keywords: ROS; cationic arginine-rich peptides (CARPs); ionotropic glutamate receptors; mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm); neuroprotection; poly-arginine-18 (R18).
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. G. MacDougall, R. Anderton, B.P. Meloni and N.W. Knuckey are shareholders in Argenica Therapeutics, which is a company developing R18 as a stroke therapeutic. The other authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis of cortical neuronal cultures treated with poly-arginine peptide-18 (R18) and exposed to glutamic acid excitotoxicity.Mol Brain. 2019 Jul 17;12(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0486-8. Mol Brain. 2019. PMID: 31315638 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro cellular uptake and neuroprotective efficacy of poly-arginine-18 (R18) and poly-ornithine-18 (O18) peptides: critical role of arginine guanidinium head groups for neuroprotection.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Jan;464(1-2):27-38. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03646-0. Epub 2019 Nov 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31679100
-
Characterisation of neuroprotective efficacy of modified poly-arginine-9 (R9) peptides using a neuronal glutamic acid excitotoxicity model.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Feb;426(1-2):75-85. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2882-z. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27844251
-
Neuroprotective peptides fused to arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides: Neuroprotective mechanism likely mediated by peptide endocytic properties.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Sep;153:36-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26048328 Review.
-
Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and Neuroprotective Peptide Therapies: A Case for Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs).Brain Sci. 2018 Aug 7;8(8):147. doi: 10.3390/brainsci8080147. Brain Sci. 2018. PMID: 30087289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modelling Epilepsy Associated Alzheimer's Disease Through Mitochondrial Complex-I Inhibition: Neurochemical and Therapeutic Perspectives.Neurochem Res. 2025 May 14;50(3):163. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04413-y. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40366471
-
The Effects of Enriched Rehabilitation on Cognitive Function and Serum Glutamate Levels Post-stroke.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 17;13:829090. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.829090. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35370905 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Poly-Arginine Peptide R18D Reduces α-Synuclein Aggregation and Uptake of α-Synuclein Seeds in Cortical Neurons.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):122. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010122. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Talantova M., Sanz-Blasco S., Zhang X., Xia P., Akhtar M.W., Okamoto S.-I., Dziewczapolski G., Nakamura T., Cao G., Pratt A.E., et al. Aβ induces astrocytic glutamate release, extrasynaptic NMDA receptor activation, and synaptic loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;113:E2518–E2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306832110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Felice F.G., Velasco P.T., Lambert M.P., Viola K., Fernandez S.J., Ferreira S.T., Klein W.L. Aβ oligomers induce neuronal oxidative stress through an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent mechanism that is blocked by the Alzheimer drug memantine. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:11590–11601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607483200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shehadeh J., Fernandes H.B., Zeron Mullins M.M., Graham R.K., Leavitt B.R., Hayden M.R., Raymond L.A. Striatal neuronal apoptosis is preferentially enhanced by NMDA receptor activation in YAC transgenic mouse model of Huntington disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006;21:392–403. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.08.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

