Microbial Natural Products as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro)
- PMID: 32610445
- PMCID: PMC7409236
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8070970
Microbial Natural Products as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro)
Abstract
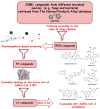
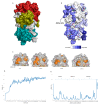
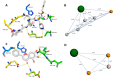
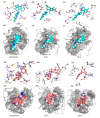
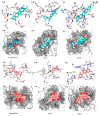
The main protease (Mpro) of the newly emerged severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was subjected to hyphenated pharmacophoric-based and structural-based virtual screenings using a library of microbial natural products (>24,000 compounds). Subsequent filtering of the resulted hits according to the Lipinski's rules was applied to select only the drug-like molecules. Top-scoring hits were further filtered out depending on their ability to show constant good binding affinities towards the molecular dynamic simulation (MDS)-derived enzyme's conformers. Final MDS experiments were performed on the ligand-protein complexes (compounds 1-12, Table S1) to verify their binding modes and calculate their binding free energy. Consequently, a final selection of six compounds (1-6) was proposed to possess high potential as anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug candidates. Our study provides insight into the role of the Mpro structural flexibility during interactions with the possible inhibitors and sheds light on the structure-based design of anti-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) therapeutics targeting SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Covid-19; Mpro; SARS-CoV-2; docking; microbial natural products; molecular dynamic simulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization Alert, Verification and Public Health Management of SARS in the Post-Outbreak Period. [(accessed on 11 June 2020)]; Available online: http://www.who.int.csr/sars/postoutbreak/en/
-
- World Health Organization Summary Table of SARS cases by Country, 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. [(accessed on 11 June 2020)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/2003_08_15/en/
-
- World Health Organization New Case of Labo- Ratory-Confirmed SARS in Guangdong, China, Update 5. [(accessed on 11 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/2004_01_31/en/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

