Protein-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems
- PMID: 32610448
- PMCID: PMC7407889
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070604
Protein-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
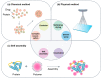
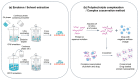
Nanoparticles have been extensively used as carriers for the delivery of chemicals and biomolecular drugs, such as anticancer drugs and therapeutic proteins. Natural biomolecules, such as proteins, are an attractive alternative to synthetic polymers commonly used in nanoparticle formulation because of their safety. In general, protein nanoparticles offer many advantages, such as biocompatibility and biodegradability. Moreover, the preparation of protein nanoparticles and the corresponding encapsulation process involved mild conditions without the use of toxic chemicals or organic solvents. Protein nanoparticles can be generated using proteins, such as fibroins, albumin, gelatin, gliadine, legumin, 30Kc19, lipoprotein, and ferritin proteins, and are prepared through emulsion, electrospray, and desolvation methods. This review introduces the proteins used and methods used in generating protein nanoparticles and compares the corresponding advantages and disadvantages of each.
Keywords: biocompatible; biodegradable; controlled release; drug delivery; protein nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rao J.P., Geckeler K.E. Polymer nanoparticles: Preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011;36:887–913. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.01.001. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

