Potential Anti-Tuberculosis Activity of the Extracts and Their Active Components of Anogeissus Leiocarpa (DC.) Guill. and Perr. with Special Emphasis on Polyphenols
- PMID: 32610461
- PMCID: PMC7399890
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9070364
Potential Anti-Tuberculosis Activity of the Extracts and Their Active Components of Anogeissus Leiocarpa (DC.) Guill. and Perr. with Special Emphasis on Polyphenols
Abstract
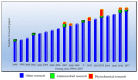
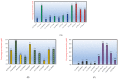
In Sudanese traditional medicine, decoctions of the stem bark of Anogeissus leiocarpa are used for the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). However, this plant has not been investigated before for its antimycobacterial effects. Our screening results show, for the first time, that many extracts of various parts of A. leiocarpa exhibit growth inhibitory activity against Mycobacterium smegmatis. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values ranged between 625 and 5000 µg/mL, with an ethyl acetate extract of the root showing the lowest MIC value. The good antimycobacterial effects of the root part could be due to its high concentration of ellagic acid derivatives, ellagitannins, and flavonoids. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) fractionation resulted in some fractions with better activity than the starting point crude methanol extract (MIC 2500 µg/mL). Those fractions with the lowest MIC values contained a high number of antioxidant compounds. Fractions 3 and 4 (MIC 1500 and 1000 µg/mL, respectively) contained high concentrations of di-methyl ellagic acid ([M-H] - 329.0318). Fraction 6 (MIC 2000 µg/mL) contained a lower concentration of di-methyl ellagic acid and was not as growth inhibitory as fractions 3 and 4. Moreover, in fraction 3, an acetylated ellagic acid derivative ([M-H] - 343.0477) and di-methyl-ellagic acid xyloside ([M-H]- 461.0739) were tentatively characterized. Di-methyl ellagic acid xyloside was also present in fraction 4 and could strongly contribute to the antimycobacterial effect of this fraction. Additionally, protocatechuic acid ([M-H]-at m/z 153.0196) was present in fraction 4. Our antimycobacterial results obtained from this research justify the use of A. leiocarpa in Sudanese folk medicine against cough related to TB. Roots, stem bark, and leaves of A. leiocarpa are sources for new potent anti-TB drug lead compounds.
Keywords: Africa; Anogeissus leiocarpa; Mycobacterium smegmatis; ellagic acid derivatives; ellagitannins; flavonoids; stilbenes; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report. World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. [(accessed on 20 February 2020)]. App Launched. Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/en/
-
- American Lung Association Learn About Tuberculosis. [(accessed on 25 December 2019)];2018 Available online: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/tuberc....
-
- Askun T. The significance of Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Tuberculosis compounds. RRJPTS. 2015:6–17.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report. World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. [(accessed on 23 December 2019)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/91355.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report. World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. [(accessed on 25 December 2019)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/gtbr2018_main_text_28F....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

