Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes
- PMID: 32610588
- PMCID: PMC7400447
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8070182
Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes
Abstract
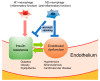
Diabetes is a worldwide health issue closely associated with cardiovascular events. Given the pandemic of obesity, the identification of the basic underpinnings of vascular disease is strongly needed. Emerging evidence has suggested that endothelial dysfunction is a critical step in the progression of atherosclerosis. However, how diabetes affects the endothelium is poorly understood. Experimental and clinical studies have illuminated the tight link between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. In addition, macrophage polarization from M2 towards M1 contributes to the process of endothelial damage. The possibility that novel classes of anti-hyperglycemic agents exert beneficial effects on the endothelial function and macrophage polarization has been raised. In this review, we discuss the current status of knowledge regarding the pathological significance of insulin signaling in endothelium. Finally, we summarize recent therapeutic strategies against endothelial dysfunction with an emphasis on macrophage polarity.
Keywords: endothelial dysfunction; insulin resistance; macrophage polarity.
Conflict of interest statement
Keiichiro Matoba has received research support from Sanofi KK, Tanabe Pharma, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. Kazunori Utsunomiya has received research support from Terumo, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Taisho Pharmaceutical, Böehringer Ingelheim, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, and Ono Pharmaceutical, as well as speaker honoraria from Tanabe Pharma, Sanofi KK, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Eli Lilly, and Böehringer Ingelheim. Rimei Nishimura has received speaker honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly Japan KK, Kissei Pharmaceutical, Medtronic Japan, MSD, Novartis Pharma KK, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Sanofi KK, and Takeda Pharmaceutical and contract research fees for collaborative research with Taisho Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Böehringer Ingelheim. All the sponsors have no role in paper processing.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition 2019. [(accessed on 20 May 2020)]; Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/resources/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

