Numerical analysis of three-dimensional echo decorrelation imaging
- PMID: 32611173
- PMCID: PMC7275868
- DOI: 10.1121/10.0001334
Numerical analysis of three-dimensional echo decorrelation imaging
Abstract
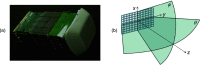
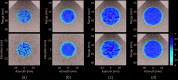
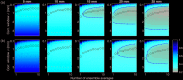
A numerical model for three-dimensional echo decorrelation imaging, a pulse-echo ultrasound method applicable to thermal ablation monitoring, is presented. Beam patterns for steered transmit and receive array apertures are combined with a three-dimensional numerical tissue model to yield beamformed scan lines in a pyramidal configuration, volumetric B-mode images, and spatial maps of normalized decorrelation between sequential image volumes. Simulated three-dimensional echo decorrelation images of random media are analyzed as estimators of local tissue reflectivity decoherence, mimicking thermal ablation effects. The estimation error is analyzed as a function of correlation window size, scan line density, and ensemble averaging of decorrelation maps.
Figures
References
-
- Puijk R. S., Ruarus A. H., Scheffer H. J., Vroomen L. G. P. H., van Tilborg A. A. J. M., de Vries J. J. J., Berger F. H., van den Tol P. M. P., and Meijerink M. R., “ Percutaneous liver tumour ablation: Image guidance, endpoint assessment, and quality control,” Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 69, 51–62 (2018).10.1016/j.carj.2017.11.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

