Biological investigations on therapeutic effect of chitosan encapsulated nano resveratrol against gestational diabetes mellitus rats induced by streptozotocin
- PMID: 32611265
- PMCID: PMC8216480
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1775722
Biological investigations on therapeutic effect of chitosan encapsulated nano resveratrol against gestational diabetes mellitus rats induced by streptozotocin
Abstract
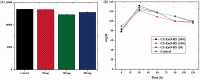
The chitosan encapsulation with bioactive compounds (resveratrol) is a significant method that can be used to raise the stability and effectiveness of substances in gestational diabetes management. In this study, the resveratrol-zinc oxide complex is encapsulated with chitosan (CS-ZnO-RS). The synthesized CS-ZnO-RS could be used to deliver the resveratrol with minimized side effects and also improved bioavailability. CS-ZnO-RS were characterized by various techniques such as particle size analyzer, DSC, FT-IR, TEM, SEM, and AFM. The electron microscopic and particle analyzer confirmed that the synthesized CS-ZnO-RS were monodispersed, spherical and its average size was 38 nm. The drug-releasing profile showed that 95% of RS is released from CS-ZnO-RS within 24 h. In vitro studies confirmed that α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activities were closely related to the concentration of CS-ZnO-RS. The highest inhibition of α-glucosidase (77.32%) and α-amylase (78.4%) was observed at 500 μg/mL. Furthermore, the treatment of CS-ZnO-RS significantly decreased the blood glucose levels in gestational diabetes mellitus induced rats and maintained the lipid content toward the normal rats. In addition, the CS-ZnO-RS reduced the level of inflammation factors (IL-6 and MCP-1) and endoplasmic reticulum stress (GRP78, p-IRE1α, p-eIF2α, and p-PERK).
Keywords: Gestational diabetes mellitus; chitosan; endoplasmic reticulum stress; resveratrol; streptozotocin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures











References
-
- Ademiluyi AO, Oboh G. (2013). Soybean phenolic-rich extracts inhibit key-enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) and hypertension (angiotensin I converting enzyme) in vitro. Exp Toxicol Pathol 65:305–9. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hussaini H, Kilarkaje N. (2018). Effects of trans-resveratrol on type 1 diabetes-induced inhibition of retinoic acid metabolism pathway in retinal pigment epithelium of Dark Agouti rats. Eur J Pharmacol 834:142–51. - PubMed
-
- Ali H, Houghton PJ, Soumyanath A. (2006). alpha-Amylase inhibitory activity of some Malaysian plants used to treat diabetes; with particular reference to Phyllanthus amarus. J Ethnopharmacol 107:449–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
