Remogliflozin Etabonate in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Design, Development, and Place in Therapy
- PMID: 32612352
- PMCID: PMC7322139
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S221093
Remogliflozin Etabonate in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Design, Development, and Place in Therapy
Abstract
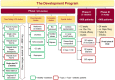
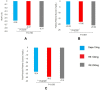
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is an emerging epidemic in Asian countries, especially in India. With the advent of the SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs demonstrating benefits beyond glycemic control, viz. weight loss, blood pressure reduction, and cardiovascular and renal protection, the management of T2DM has taken a quantum leap. Remogliflozin etabonate (RE) is the latest addition to the SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs that have been recently approved in India for the management of T2DM. RE is a potent and selective inhibitor of SGLT2 with the unique distinction of being administered as a prodrug, existence of active metabolites, and short half-life necessitating twice-daily dosing. The Phase III study of RE demonstrated it to be an efficacious and safe agent and non-inferior to the currently available SGLT2 inhibitors. This paper reviews not only the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, and safety profile of RE but also its molecular and clinical development program. This review has taken into consideration all available published as well as unpublished literature on RE and discusses the individual studies performed during its development for characterization of pharmacological profile.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitor; T2DM; design; development; etabonate; place in therapy; remogliflozin.
© 2020 Mohan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Viswanathan Mohan and all other authors of this manuscript report personal fees as an Advisory Board Member of Glenmark Pharmaceuticals which markets Remogliflozin in India, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas 9th edition; 2019. Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/resources/.Accessed December20, 2019.
-
- Dey L, Attele AS, Yuan CS. Alternative therapies for type 2 diabetes. Altern Med Rev. 2002;7(1):45–58. - PubMed
-
- Tamez-Perez HE, Gonzalez-Guajardo EE, Tamez-Pena AL. Consensus statement by The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - 2019 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2019;25(6):622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

