Cortical ChAT+ neurons co-transmit acetylcholine and GABA in a target- and brain-region-specific manner
- PMID: 32613945
- PMCID: PMC7360370
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57749
Cortical ChAT+ neurons co-transmit acetylcholine and GABA in a target- and brain-region-specific manner
Abstract
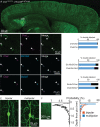
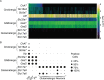
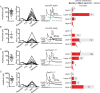
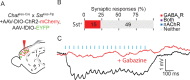
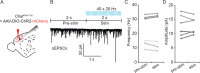
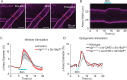
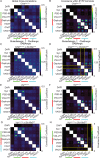
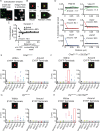
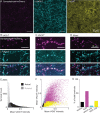
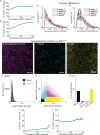
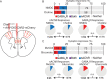
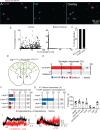
The mouse cerebral cortex contains neurons that express choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and are a potential local source of acetylcholine. However, the neurotransmitters released by cortical ChAT+ neurons and their synaptic connectivity are unknown. We show that the nearly all cortical ChAT+ neurons in mice are specialized VIP+ interneurons that release GABA strongly onto other inhibitory interneurons and acetylcholine sparsely onto layer 1 interneurons and other VIP+/ChAT+ interneurons. This differential transmission of ACh and GABA based on the postsynaptic target neuron is reflected in VIP+/ChAT+ interneuron pre-synaptic terminals, as quantitative molecular analysis shows that only a subset of these are specialized to release acetylcholine. In addition, we identify a separate, sparse population of non-VIP ChAT+ neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex with a distinct developmental origin that robustly release acetylcholine in layer 1. These results demonstrate both cortex-region heterogeneity in cortical ChAT+ interneurons and target-specific co-release of acetylcholine and GABA.
Keywords: Acetylcholine; GABA; VIP; cortical interneurons; mouse; neuromodulation; neuroscience; neurotransmitter co-release.
© 2020, Granger et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AG, WW, KR, ME, AZ, KB, AS, BC, VN, MT, CH, CG, BS No competing interests declared
Figures






References
-
- Bayraktar T, Staiger JF, Acsady L, Cozzari C, Freund TF, Zilles K. Co-localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, gamma-aminobutyric acid and choline acetyltransferase in neocortical interneurons of the adult rat. Brain Research. 1997;757:209–217. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(97)00218-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

